HCV drug discovery aimed at viral eradication
- PMID: 20040045
- PMCID: PMC4064679
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2009.01246.x
HCV drug discovery aimed at viral eradication
Abstract
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) causes significant morbidity and mortality worldwide with nearly 3% of the world population infected by this virus. Fortunately, this virus does not establish latency, and hence it may be possible to eradicate it. HCV is strongly associated with liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma and is currently treated with pegylated interferon-alpha (peg-IFN-alpha) and ribavirin. Unfortunately, these limited treatment options often produce significant side effects, and currently, complete eradication of virus with combined drug modalities has not yet been achieved for the majority of chronically HCV-infected individuals. Restricted treatment options, lack of a universal cure for HCV and the link between chronic infection, liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma necessitate design of novel drugs and treatment options. Understanding the relationship between the immune response, viral clearance and inhibition of viral replication with pharmacology-based design can ultimately allow for complete eradication of HCV. This review focuses upon significant novel preclinical and clinical specifically targeted antiviral therapy (STAT-C) drugs under development, highlights their mechanism of action, and discusses their impact on systemic viral loads and permanent clearance of infection.
Figures

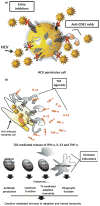
References
-
- Heathcote J, Main J. Treatment of hepatitis C. J Viral Hepat. 2005;12(3):223–235. - PubMed
-
- Kim AI, Saab S. Treatment of hepatitis C. Am J Med. 2005;118(8):808–815. - PubMed
-
- Zaman A, Fennerty MB, Keeffe EB. Systematic review: peg-interferon vs. standard interferon in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003;18(7):661–670. - PubMed
-
- Schinazi RF, Sommadossi JP, Thomas H. Therapies for Viral Hepatitis. London: International Medical Press; 1998.
-
- Simmonds P, Holmes EC, Cha TA, et al. Classification of hepatitis C virus into six major genotypes and a series of subtypes by phylogenetic analysis of the NS-5 region. J Gen Virol. 1993;74(Pt 11):2391–2399. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

