Structural abnormality of the substantia nigra in children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder
- PMID: 20040247
- PMCID: PMC2799505
- DOI: 10.1503/jpn.090044
Structural abnormality of the substantia nigra in children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder
Abstract
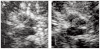
Background: Structural abnormality of the substantia nigra can be detected by transcranial sonography in neuropsychiatric disorders such as Parkinson disease and restless legs syndrome. We investigated echogenicity of the substantia nigra as a potential structural marker for dysfunction of the nigrostriatal dopamine system in children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Methods: We used a blinded design and determined echogenicity of the substantia nigra by use of transcranial sonography in 22 children with ADHD and 22 healthy controls matched for age and sex.
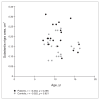
Results: The echogenic substantia nigra area was significantly larger in ADHD patients than in healthy controls (F(1,42) = 9.298, p = 0.004, effect size = 0.92). We found no effects of age or sex.
Limitations: Owing to a lack of dimensional assessment, we could not analyze the correlation between echogenicity and clinical symptoms.
Conclusion: Our results support the hypothesis that the nigrostriatal dopaminergic system is abnormal in children with ADHD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased echogenicity of the substantia nigra in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.Biol Psychiatry. 2010 Aug 15;68(4):352-8. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.01.013. Epub 2010 Mar 15. Biol Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 20227683
-
Preliminary Study of ADHD Biomarkers in Adults with Focus on Serum Iron and Transcranial Sonography of the Substantia Nigra.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 May 3;18(9):4875. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18094875. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34063655 Free PMC article.
-
Severity of restless legs syndrome is inversely correlated with echogenicity of the substantia nigra in different neurodegenerative movement disorders. a preliminary observation.J Neurol Sci. 2012 Aug 15;319(1-2):59-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2012.05.015. Epub 2012 May 24. J Neurol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22632781
-
Transcranial sonography in Parkinson's disease.Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2012 Apr-Jun;10(2):242-6. doi: 10.1590/s1679-45082012000200022. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2012. PMID: 23052464 Review. English, Portuguese.
-
[Transcranial sonography of substantia nigra in patients with Parkinson's disease].Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2013;53(11):981-2. doi: 10.5692/clinicalneurol.53.981. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2013. PMID: 24291852 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Time perception impairs sensory-motor integration in Parkinson's disease.Int Arch Med. 2013 Oct 16;6(1):39. doi: 10.1186/1755-7682-6-39. Int Arch Med. 2013. PMID: 24131660 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of anesthetics on substantia nigra tyrosine hydroxylase expression and tau phosphorylation in the hypoxic-ischemic near-term lamb.Pediatr Res. 2018 Jun;83(6):1190-1199. doi: 10.1038/pr.2018.42. Epub 2018 May 9. Pediatr Res. 2018. PMID: 29741516
-
ADHD pathogenesis in the immune, endocrine and nervous systems of juvenile and maturating SHR and WKY rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Oct;236(10):2937-2958. doi: 10.1007/s00213-019-5180-0. Epub 2019 Feb 8. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30737597 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the ADHD candidate gene Diras2 in the brain.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2018 Jun;125(6):913-923. doi: 10.1007/s00702-018-1867-3. Epub 2018 Feb 27. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2018. PMID: 29488099
-
Individualised stepwise adaptive treatment for 3-6-year-old preschool children impaired by attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ESCApreschool): study protocol of an adaptive intervention study including two randomised controlled trials within the consortium ESCAlife.Trials. 2020 Jan 9;21(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s13063-019-3872-8. Trials. 2020. PMID: 31918739 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Polanczyk G, de Lima MS, Horta BL, et al. The worldwide prevalence of ADHD: a systematic review and metaregression analysis. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164:942–8. - PubMed
-
- Biederman J, Faraone SV. Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Lancet. 2005;366:237–48. - PubMed
-
- Mehler-Wex C, Riederer P, Gerlach M. Dopaminergic dysbalance in distinct basal ganglia neurocircuits: implications for the pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease, schizophrenia and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Neurotox Res. 2006;10:167–79. - PubMed
-
- Becker G, Seufert J, Bogdahn U, et al. Degeneration of substantia nigra in chronic Parkinson’s disease visualized by transcranial color-coded real-time sonography. Neurology. 1995;45:182–4. - PubMed
-
- Berg D, Godau J, Walter U. Transcranial sonography in movement disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7:1044–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
