Rfx6 is an Ngn3-dependent winged helix transcription factor required for pancreatic islet cell development
- PMID: 20040487
- PMCID: PMC2799156
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.041673
Rfx6 is an Ngn3-dependent winged helix transcription factor required for pancreatic islet cell development
Abstract
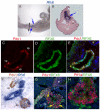
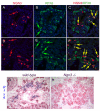
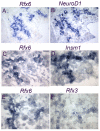
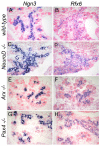
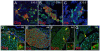
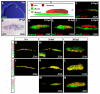
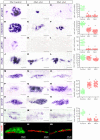
The transcription factor neurogenin 3 (Neurog3 or Ngn3) controls islet cell fate specification in multipotent pancreatic progenitor cells in the mouse embryo. However, our knowledge of the genetic programs implemented by Ngn3, which control generic and islet subtype-specific properties, is still fragmentary. Gene expression profiling in isolated Ngn3-positive progenitor cells resulted in the identification of the uncharacterized winged helix transcription factor Rfx6. Rfx6 is initially expressed broadly in the gut endoderm, notably in Pdx1-positive cells in the developing pancreatic buds, and then becomes progressively restricted to the endocrine lineage, suggesting a dual function in both endoderm development and islet cell differentiation. Rfx6 is found in postmitotic islet progenitor cells in the embryo and is maintained in all developing and adult islet cell types. Rfx6 is dependent on Ngn3 and acts upstream of or in parallel with NeuroD, Pax4 and Arx transcription factors during islet cell differentiation. In zebrafish, the Rfx6 ortholog is similarly found in progenitors and hormone expressing cells of the islet lineage. Loss-of-function studies in zebrafish revealed that rfx6 is required for the differentiation of glucagon-, ghrelin- and somatostatin-expressing cells, which, in the absence of rfx6, are blocked at the progenitor stage. By contrast, beta cells, whose number is only slightly reduced, were no longer clustered in a compact islet. These data unveil Rfx6 as a novel regulator of islet cell development.
Figures
References
-
- Ahlgren U., Pfaff S. L., Jessell T. M., Edlund T., Edlund H. (1997). Independent requirement for ISL1 in formation of pancreatic mesenchyme and islet cells. Nature 385, 257-260 - PubMed
-
- Ait-Lounis A., Baas D., Barras E., Benadiba C., Charollais A., Nlend N. R., Liegeois D., Meda P., Durand B., Reith W. (2007). Novel function of the ciliogenic transcription factor RFX3 in development of the endocrine pancreas. Diabetes 56, 950-959 - PubMed
-
- Argenton F., Zecchin E., Bortolussi M. (1999). Early appearance of pancreatic hormone-expressing cells in the zebrafish embryo. Mech. Dev. 87, 217-221 - PubMed
-
- Biemar F., Argenton F., Schmidtke R., Epperlein S., Peers B., Driever W. (2001). Pancreas development in zebrafish: early dispersed appearance of endocrine hormone expressing cells and their convergence to form the definitive islet. Dev. Biol. 230, 189-203 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

