A planarian p53 homolog regulates proliferation and self-renewal in adult stem cell lineages
- PMID: 20040488
- PMCID: PMC2799157
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.044297
A planarian p53 homolog regulates proliferation and self-renewal in adult stem cell lineages
Abstract
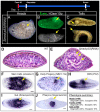
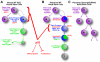
The functions of adult stem cells and tumor suppressor genes are known to intersect. However, when and how tumor suppressors function in the lineages produced by adult stem cells is unknown. With a large population of stem cells that can be manipulated and studied in vivo, the freshwater planarian is an ideal system with which to investigate these questions. Here, we focus on the tumor suppressor p53, homologs of which have no known role in stem cell biology in any invertebrate examined thus far. Planaria have a single p53 family member, Smed-p53, which is predominantly expressed in newly made stem cell progeny. When Smed-p53 is targeted by RNAi, the stem cell population increases at the expense of progeny, resulting in hyper-proliferation. However, ultimately the stem cell population fails to self-renew. Our results suggest that prior to the vertebrates, an ancestral p53-like molecule already had functions in stem cell proliferation control and self-renewal.
Figures
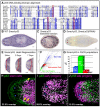
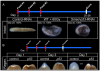
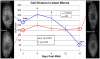

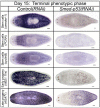
Similar articles
-
The Retinoblastoma pathway regulates stem cell proliferation in freshwater planarians.Dev Biol. 2013 Jan 15;373(2):442-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.10.025. Epub 2012 Nov 1. Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23123964
-
Argonaute-2 regulates the proliferation of adult stem cells in planarian.Cell Res. 2011 Dec;21(12):1750-4. doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.151. Epub 2011 Sep 6. Cell Res. 2011. PMID: 21894189 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
An RbAp48-like gene regulates adult stem cells in planarians.J Cell Sci. 2010 Mar 1;123(Pt 5):690-8. doi: 10.1242/jcs.053900. Epub 2010 Feb 2. J Cell Sci. 2010. PMID: 20124416
-
The emerging functions of the p53-miRNA network in stem cell biology.Cell Cycle. 2012 Jun 1;11(11):2063-72. doi: 10.4161/cc.20207. Epub 2012 Jun 1. Cell Cycle. 2012. PMID: 22580472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Molecular approach to planarian stem cell system].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2005 May;50(6 Suppl):706-10. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2005. PMID: 15926503 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Transposon control as a checkpoint for tissue regeneration.Development. 2022 Nov 15;149(22):dev191957. doi: 10.1242/dev.191957. Epub 2022 Nov 28. Development. 2022. PMID: 36440631 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular hyperproliferation and cancer as evolutionary variables.Curr Biol. 2012 Sep 11;22(17):R772-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.08.008. Curr Biol. 2012. PMID: 22975008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Genome of the Softshell Clam Mya arenaria and the Evolution of Apoptosis.Genome Biol Evol. 2020 Oct 1;12(10):1681-1693. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evaa143. Genome Biol Evol. 2020. PMID: 32653903 Free PMC article.
-
Convergent evolution of a genotoxic stress response in a parasite-specific p53 homolog.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Sep 13;119(37):e2205201119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2205201119. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36067283 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage and tissue repair: What we can learn from planaria.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Mar;87:145-159. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.04.013. Epub 2018 May 3. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 29727725 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brodsky M. H., Nordstrom W., Tsang G., Kwan E., Rubin G. M., Abrams J. M. (2000). Drosophila p53 binds a damage response element at the reaper locus. Cell 101, 103-113 - PubMed
-
- Derry W. B., Putzke A. P., Rothman J. H. (2001). Caenorhabditis elegans p53: role in apoptosis, meiosis, and stress resistance. Science 294, 591-595 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

