Non-cell-autonomous retinoid signaling is crucial for renal development
- PMID: 20040494
- PMCID: PMC2799161
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.040287
Non-cell-autonomous retinoid signaling is crucial for renal development
Abstract
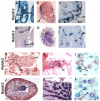
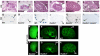
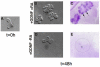
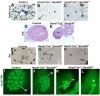
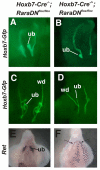
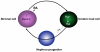
In humans and mice, mutations in the Ret gene result in Hirschsprung's disease and renal defects. In the embryonic kidney, binding of Ret to its ligand, Gdnf, induces a program of epithelial cell remodeling that controls primary branch formation and branching morphogenesis within the kidney. Our previous studies showed that transcription factors belonging to the retinoic acid (RA) receptor family are crucial for controlling Ret expression in the ureteric bud; however, the mechanism by which retinoid-signaling acts has remained unclear. In the current study, we show that expression of a dominant-negative RA receptor in mouse ureteric bud cells abolishes Ret expression and Ret-dependent functions including ureteric bud formation and branching morphogenesis, indicating that RA-receptor signaling in ureteric bud cells is crucial for renal development. Conversely, we find that RA-receptor signaling in ureteric bud cells depends mainly on RA generated in nearby stromal cells by retinaldehyde dehydrogenase 2, an enzyme required for most fetal RA synthesis. Together, these studies suggest that renal development depends on paracrine RA signaling between stromal mesenchyme and ureteric bud cells that regulates Ret expression both during ureteric bud formation and within the developing collecting duct system.
Figures

References
-
- Batourina E., Gim S., Bello N., Shy M., Clagett-Dame M., Srinivas S., Costantini F., Mendelsohn C. (2001). Vitamin A controls epithelial/mesenchymal interactions through Ret expression. Nat. Genet. 27, 74-78 - PubMed
-
- Batourina E., Tsai S., Lambert S., Sprenkle P., Viana R., Dutta S., Hensle T., Wang F., Niederreither K., McMahon A. P., et al. (2005). Apoptosis induced by vitamin A signaling is crucial for connecting the ureters to the bladder. Nat. Genet. 37, 1082-1089 - PubMed
-
- Bhat P. V., Manolescu D. C. (2008). Role of vitamin A in determining nephron mass and possible relationship to hypertension. J. Nutr. 138, 1407-1410 - PubMed
-
- Blumberg B., Bolado J., Jr, Moreno T. A., Kintner C., Evans R. M., Papalopulu N. (1997). An essential role for retinoid signaling in anteroposterior neural patterning. Development 124, 373-379 - PubMed
-
- Brenner B. M., Mackenzie H. S. (1997). Nephron mass as a risk factor for progression of renal disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 63, S124-S127 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

