Movement and remodeling of the endoplasmic reticulum in nondividing cells of tobacco leaves
- PMID: 20040535
- PMCID: PMC2814503
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.109.072249
Movement and remodeling of the endoplasmic reticulum in nondividing cells of tobacco leaves
Abstract
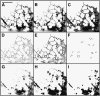
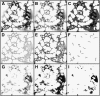
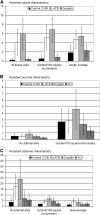
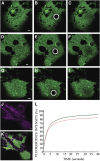
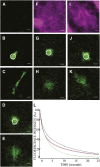
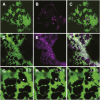
Using a novel analytical tool, this study investigates the relative roles of actin, microtubules, myosin, and Golgi bodies on form and movement of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) leaf epidermal cells. Expression of a subset of truncated class XI myosins, which interfere with the activity of native class XI myosins, and drug-induced actin depolymerization produce a more persistent network of ER tubules and larger persistent cisternae. The treatments differentially affect two persistent size classes of cortical ER cisternae, those >0.3 microm(2) and those smaller, called punctae. The punctae are not Golgi, and ER remodeling occurs in the absence of Golgi bodies. The treatments diminish the mobile fraction of ER membrane proteins but not the diffusive flow of mobile membrane proteins. The results support a model whereby ER network remodeling is coupled to the directionality but not the magnitude of membrane surface flow, and the punctae are network nodes that act as foci of actin polymerization, regulating network remodeling through exploratory tubule growth and myosin-mediated shrinkage.
Figures


References
-
- Adam, G., and Delbruck, M. (1968). Reduction of dimensionality in biological diffusion processes. In Structural Chemistry in Molecular Biology, A. Rich and N. Davidson, eds (San Francisco, CA: Freeman), pp. 198–215.
-
- Boevink, P., Martin, B., Oparka, K., Santa Cruz, S., and Hawes, C. (1999). Transport of virally expressed green fluorescent protein through the secretory pathway in tobacco leaves is inhibited by cold shock and brefeldin A. Planta 208 392–400.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

