Two types of meiotic crossovers coexist in maize
- PMID: 20040539
- PMCID: PMC2814511
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.109.071514
Two types of meiotic crossovers coexist in maize
Abstract
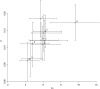
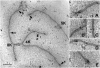
We apply modeling approaches to investigate the distribution of late recombination nodules in maize (Zea mays). Such nodules indicate crossover positions along the synaptonemal complex. High-quality nodule data were analyzed using two different interference models: the "statistical" gamma model and the "mechanical" beam film model. For each chromosome, we exclude at a 98% significance level the hypothesis that a single pathway underlies the formation of all crossovers, pointing to the coexistence of two types of crossing-over in maize, as was previously demonstrated in other organisms. We estimate the proportion of crossovers coming from the noninterfering pathway to range from 6 to 23% depending on the chromosome, with a cell average of approximately 15%. The mean number of noninterfering crossovers per chromosome is significantly correlated with the length of the synaptonemal complex. We also quantify the intensity of interference. Finally, we develop inference tools that allow one to tackle, without much loss of power, complex crossover interference models such as the beam film. The lack of a likelihood function in such models had prevented their use for parameter estimation. This advance will allow more realistic mechanisms of crossover formation to be modeled in the future.
Figures


References
-
- Anderson, L.K., and Stack, S.M. (2002). Meiotic recombination in plants. Curr. Genomics 3 507–525.
-
- Anderson, L.K., Stack, S.M., Fox, M.H., and Zhang, C.S. (1985). The relationship between genome size and synaptonemal complex length in higher plants. Exp. Cell Res. 156 367–378. - PubMed
-
- Basheva, E., Bidau, C., and Borodin, P. (2008). General pattern of meiotic recombination in male dogs estimated by MLH1 and RAD51 immunolocalization. Chromosome Res. 16 709–719. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

