Rearrangement of the RNA polymerase subunit H and the lower jaw in archaeal elongation complexes
- PMID: 20040576
- PMCID: PMC2847245
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp1190
Rearrangement of the RNA polymerase subunit H and the lower jaw in archaeal elongation complexes
Abstract
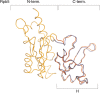
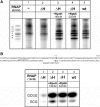
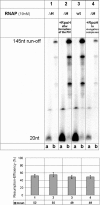
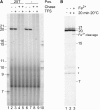
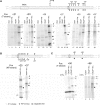
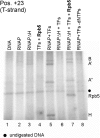
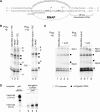
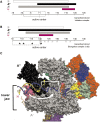
The lower jaws of archaeal RNA polymerase and eukaryotic RNA polymerase II include orthologous subunits H and Rpb5, respectively. The tertiary structure of H is very similar to the structure of the C-terminal domain of Rpb5, and both subunits are proximal to downstream DNA in pre-initiation complexes. Analyses of reconstituted euryarchaeal polymerase lacking subunit H revealed that H is important for open complex formation and initial transcription. Eukaryotic Rpb5 rescues activity of the DeltaH enzyme indicating a strong conservation of function for this subunit from archaea to eukaryotes. Photochemical cross-linking in elongation complexes revealed a striking structural rearrangement of RNA polymerase, bringing subunit H near the transcribed DNA strand one helical turn downstream of the active center, in contrast to the positioning observed in preinitiation complexes. The rearrangement of subunits H and A'' suggest a major conformational change in the archaeal RNAP lower jaw upon formation of the elongation complex.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mutational studies of archaeal RNA polymerase and analysis of hybrid RNA polymerases.Biochem Soc Trans. 2009 Feb;37(Pt 1):18-22. doi: 10.1042/BST0370018. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009. PMID: 19143595
-
Evolution of complex RNA polymerases: the complete archaeal RNA polymerase structure.PLoS Biol. 2009 May;7(5):e1000102. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000102. Epub 2009 May 5. PLoS Biol. 2009. PMID: 19419240 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-protein interactions in the archaeal transcriptional machinery: binding studies of isolated RNA polymerase subunits and transcription factors.J Biol Chem. 2006 Oct 13;281(41):30581-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M605209200. Epub 2006 Aug 1. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16885163
-
Determinants of transcription initiation by archaeal RNA polymerase.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2005 Dec;8(6):677-84. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2005.10.016. Epub 2005 Oct 24. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16249119 Review.
-
Multisubunit RNA polymerases.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2002 Feb;12(1):89-97. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(02)00294-4. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2002. PMID: 11839495 Review.
Cited by
-
Evolution of multisubunit RNA polymerases in the three domains of life.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011 Feb;9(2):85-98. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2507. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21233849 Review.
-
Fidelity in archaeal information processing.Archaea. 2010 Sep 5;2010:960298. doi: 10.1155/2010/960298. Archaea. 2010. PMID: 20871851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of a chimeric Rpb5/RpoH subunit using library selection.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 29;9(1):e87485. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087485. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24489922 Free PMC article.
-
Rpb5, a subunit shared by eukaryotic RNA polymerases, cooperates with prefoldin-like Bud27/URI.AIMS Genet. 2018 Feb 27;5(1):63-74. doi: 10.3934/genet.2018.1.74. eCollection 2018. AIMS Genet. 2018. PMID: 31435513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Displacement of the transcription factor B reader domain during transcription initiation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Nov 2;46(19):10066-10081. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky699. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 30102372 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hausner W, Wettach J, Hethke C, Thomm M. Two transcription factors related with the eucaryal transcription factors TATA-binding protein and transcription factor IIB direct promoter recognition by an archaeal RNA polymerase. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:30144–30148. - PubMed
-
- Bell SD, Jackson P. The role of transcription factor B in transcription initiation and promoter clearance in the Archaeon Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:12934–12940. - PubMed
-
- Meinhart AJ, Blobel J, Cramer P. An extended winged helix domain in general transcription factor E/IIEalpha. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:48267–48274. - PubMed

