Newborn screening for cystic fibrosis by use of a multiplex immunoassay
- PMID: 20040620
- PMCID: PMC3227416
- DOI: 10.1373/clinchem.2009.132480
Newborn screening for cystic fibrosis by use of a multiplex immunoassay
Abstract
Background: Since its beginnings, newborn screening for cystic fibrosis (CF) using an assay for immunoreactive trypsinogen (IRT) has been plagued by a high rate of false-positive results (screen positive, diagnosis negative), despite attempts to reduce this rate by use of altered cutoffs and second-tier DNA testing. IRT exists as 2 isoforms: IRT1 and IRT2, with IRT2 being more closely aligned with pancreatic disease, including CF. Assay standardization between programs is a continuing problem because the IRT assays currently in use variously recognize either 1 or both isoforms. Here we report the development of a multiplexed assay for both forms of IRT simultaneously.
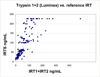
Methods: Using 2 different Luminex bead sets, we developed assays for each IRT isoform separately and then combined them. Using the sum of IRT1 and IRT2 values (IRT1+IRT2), we compared the results with a CF kit currently in use.
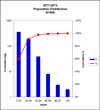
Results: In a sample set consisting of 16 cases confirmed positive for CF, we established a cutoff at >97 microg/L total IRT. Seven of 8 carriers with 1 CF mutation screen-positive by the standard method were also screen-positive by IRT1+IRT2. Of 32 cases screen-positive by standard IRT, 11 were screen-negative by IRT1+IRT2. None of these 11 cases had CF mutations identified by the screening program.
Conclusions: These data indicate that the multiplex method with specificity for 2 isoforms of IRT has performance comparable to that of a standard IRT method and the advantage of improved standardization by detection of the 2 isoforms.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IRT/IRT as a newborn cystic fibrosis screening method: optimal cutoff points for a mixed population.Cad Saude Publica. 2024 Aug 26;40(7):e00150623. doi: 10.1590/0102-311XEN150623. eCollection 2024. Cad Saude Publica. 2024. PMID: 39194088 Free PMC article.
-
Cost effectiveness of newborn screening for cystic fibrosis: a simulation study.J Cyst Fibros. 2014 May;13(3):267-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2013.10.012. Epub 2013 Nov 12. J Cyst Fibros. 2014. PMID: 24238947
-
Development of mutant human immunoreactive trypsinogen 1 (IRT1) and mutant human immunoreactive trypsinogen 2 (IRT2) for use in immunoassays.Protein Expr Purif. 2020 May;169:105572. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2020.105572. Epub 2020 Jan 21. Protein Expr Purif. 2020. PMID: 31972264
-
Evaluation of specificity and sensitivity of IRT/IRT protocol in the cystic fibrosis newborn screening program: 6-year experience of three tertiary centers.Eur J Pediatr. 2023 Mar;182(3):1067-1076. doi: 10.1007/s00431-022-04766-4. Epub 2022 Dec 24. Eur J Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 36565324
-
Severe lung disease in children with cystic fibrosis missed in newborn screening.Pediatr Pulmonol. 2024 Jan;59(1):163-168. doi: 10.1002/ppul.26734. Epub 2023 Oct 27. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2024. PMID: 37888495 Review.
Cited by
-
A multiplex immunoassay using the Guthrie specimen to detect T-cell deficiencies including severe combined immunodeficiency disease.Clin Chem. 2010 Sep;56(9):1460-5. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2010.144329. Epub 2010 Jul 21. Clin Chem. 2010. PMID: 20660143 Free PMC article.
-
Variants in Solute Carrier SLC26A9 Modify Prenatal Exocrine Pancreatic Damage in Cystic Fibrosis.J Pediatr. 2015 May;166(5):1152-1157.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2015.01.044. Epub 2015 Mar 11. J Pediatr. 2015. PMID: 25771386 Free PMC article.
-
Newborn screening for autism: in search of candidate biomarkers.Biomark Med. 2013 Apr;7(2):247-60. doi: 10.2217/bmm.12.108. Biomark Med. 2013. PMID: 23547820 Free PMC article.
-
Multiplex method for simultaneous serological detection of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus and porcine circovirus type 2.J Clin Microbiol. 2011 Sep;49(9):3184-90. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00557-11. Epub 2011 Jul 6. J Clin Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21734031 Free PMC article.
-
Frequency of Usher syndrome in two pediatric populations: Implications for genetic screening of deaf and hard of hearing children.Genet Med. 2010 Aug;12(8):512-6. doi: 10.1097/GIM.0b013e3181e5afb8. Genet Med. 2010. PMID: 20613545 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crossley JR, Elliott RB, Smith PA. Dried blood spot screening for cystic fibrosis in the newborn. Lancet. 1979;1:742–744. - PubMed
-
- Guy O, Lombardo D, Bartelt DC, Amic J, Figarella C. Two human trypsinogens: purification, molecular properties and N-Terminal sequences. Biochemistry. 1978;17(9):1669–1675. - PubMed
-
- Kimland M, Russick C, Marks WH, Borgstrom A. Immunoreactive anionic and cationic trypsin in human serum. Clin Chim Acta. 1989;184:31–46. - PubMed
-
- Itkonen O, Koivunen E, Hurme M, Alfthan H, Schroder T, Stenman U-H. Time resolved immunofluorometric assays for trypsinogen 1 and 2 in serum reveal preferential elevation of trypsinogen-2 in pancreatitis. J Lab Clin Med. 1990;115:712–718. - PubMed
-
- Deam SM, Ryley HC. Enzyme imunoassay of immunoreactive trypsin in serum and blood spots. Wein Klin Wochenschr. 1988;100:55–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous