Assessment of vitamin B(12) absorption based on the accumulation of orally administered cyanocobalamin on transcobalamin
- PMID: 20040621
- PMCID: PMC10594690
- DOI: 10.1373/clinchem.2009.131524
Assessment of vitamin B(12) absorption based on the accumulation of orally administered cyanocobalamin on transcobalamin
Abstract
Background: Vitamin B(12), or cobalamin (Cbl), is absorbed in the intestine and transported to the cells bound to transcobalamin (TC). We hypothesize that cyanocobalamin (CNCbl) is absorbed unchanged, thereby allowing measurement of the complex of CNCbl bound to TC (TC-CNCbl) to be used for studying the absorption of the vitamin.
Methods: TC was immunoprecipitated from serum samples obtained from healthy donors at baseline and at 24 h after oral administration of three 9-microg CNCbl doses over 1 day. Cbl was released by treatment with subtilisin Carlsberg. The different forms of Cbl were isolated by HPLC and subsequently quantified with an ELISA-based Cbl assay.
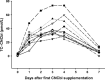
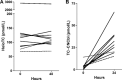
Results: At baseline, the median TC-CNCbl concentration was 1 pmol/L (range, 0-10 pmol/L); the intraindividual variation (SD) was 1.6 pmol/L (n = 31). After CNCbl administration, the TC-CNCbl concentration increased significantly (P = 0.0003, paired t-test), whereas no major changes were observed in any of the other Cbl forms bound to TC (n = 10). Only a moderate additional increase in TC-CNCbl was observed with prolonged (5 days) CNCbl administration (n = 10). We designed an absorption test based on measuring TC-CNCbl at baseline and 24 h after CNCbl intake and established a reference interval for the increase in TC-CNCbl (n = 78). The median absolute increase was 23 pmol/L (range, 6-64 pmol/L), and the relative increase was >3-fold.
Conclusions: Our data demonstrate that CNCbl is absorbed unchanged and accumulates on circulating TC. We suggest that measuring TC-CNCbl will improve the assessment of vitamin B(12) absorption.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Holo-transcobalamin concentration and transcobalamin saturation reflect recent vitamin B12 absorption better than does serum vitamin B12.Clin Chem. 2004 Jun;50(6):1043-9. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2003.027458. Epub 2004 Mar 25. Clin Chem. 2004. PMID: 15044317
-
Absorption and retention of free and milk protein-bound cyano- and hydroxocobalamins. An experimental study in rats.Biochimie. 2016 Jul;126:57-62. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2015.11.024. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Biochimie. 2016. PMID: 26626348
-
Holo-transcobalamin is an indicator of vitamin B-12 absorption in healthy adults with adequate vitamin B-12 status.Am J Clin Nutr. 2007 Apr;85(4):1057-61. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/85.4.1057. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007. PMID: 17413105
-
Receptor-mediated endocytosis of cobalamin (vitamin B12).Annu Rev Nutr. 1999;19:173-95. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nutr.19.1.173. Annu Rev Nutr. 1999. PMID: 10448521 Review.
-
Cobalamin transport proteins and their cell-surface receptors.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2003 Jun 13;5(18):1-18. doi: 10.1017/S1462399403006422. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2003. PMID: 14585166 Review.
Cited by
-
Juvenile selective vitamin B₁₂ malabsorption: 50 years after its description-10 years of genetic testing.Pediatr Res. 2011 Sep;70(3):222-8. doi: 10.1203/PDR.0b013e3182242124. Pediatr Res. 2011. PMID: 21623254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differences in Tissue Distribution of Cyano⁻B12 and Hydroxo⁻B12 One Week after Oral Intake: An Experimental Study in Male Wistar Rats.Nutrients. 2018 Oct 12;10(10):1487. doi: 10.3390/nu10101487. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30322035 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue distribution of oral vitamin B12 is influenced by B12 status and B12 form: an experimental study in rats.Eur J Nutr. 2018 Jun;57(4):1459-1469. doi: 10.1007/s00394-017-1424-0. Epub 2017 Mar 20. Eur J Nutr. 2018. PMID: 28321545 Free PMC article.
-
Inherited cobalamin malabsorption. Mutations in three genes reveal functional and ethnic patterns.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2012 Aug 28;7:56. doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-7-56. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2012. PMID: 22929189 Free PMC article.
-
Cyano-B12 or Whey Powder with Endogenous Hydroxo-B12 for Supplementation in B12 Deficient Lactovegetarians.Nutrients. 2019 Oct 6;11(10):2382. doi: 10.3390/nu11102382. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31590426 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Nexo E. Cobalamin binding proteins. Kräutler B Arigoni D Golding BT eds. Vitamin B12 and B12-binding proteins 1998:p 461-475 Wiley-VCH Weinheim (Germany). .
-
- Birn H, Verroust PJ, Nexo E, Hager H, Jacobsen C, Christensen EI, Moestrup SK. Characterization of an epithelial ∼460-kDa protein that facilitates endocytosis of intrinsic factor-vitamin B12 and binds receptor-associated protein. J Biol Chem 1997;272:26497-26504PubMed uses this format: “approximately 460-kDa.”. - PubMed
-
- Herzlich B, Herbert V. Depletion of serum holotranscobalamin II. An early sign of negative vitamin B12 balance. Lab Invest 1988;58:332-337. - PubMed
-
- England JM, Down MC, Wise IJ, Linnell JC. The transport of endogenous vitamin B12 in normal human serum. Clin Sci Mol Med 1976;51:47-52. - PubMed
-
- Hall CA. The carriers of native vitamin B12 in normal human serum. Clin Sci Mol Med 1977;53:453-457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

