The role of exhaust ventilation systems in reducing occupational exposure to organic solvents in a paint manufacturing factory
- PMID: 20040984
- PMCID: PMC2796753
- DOI: 10.4103/0019-5278.43266
The role of exhaust ventilation systems in reducing occupational exposure to organic solvents in a paint manufacturing factory
Abstract
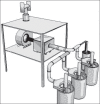
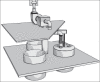
This paper presents the successful design and implementation of several exhaust ventilation systems in a paint manufacturing factory. The ventilation systems were designed based on American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists recommendations. The duct works, fans, and other parts were made and mounted by local manufacturers. The concentrations of toluene and xylene as the common solvents used in paint mixing factories were measured to evaluate the role of ventilation systems in controlling the organic solvents. Occupational exposure to toluene and xylene as the major pollutants was assessed with and without applying ventilation systems. For this purpose, samples were taken from breathing zone of exposed workers using personal samples. The samples were analyzed using Occupational Safety and Health Administration analytical method No.12. The samples were quantified using gas chromatography. The results showed that the ventilation systems successfully controlled toluene and xylene vapors in workplace, air well below the recommended threshold limit value of Iran (44.49 and 97.73 ppm, respectively). It was also discovered that benzene concentration in workplace air was higher than its allowable concentrations. This could be from solvents impurities that require more investigations.
Keywords: Exhaust ventilation systems; occupational exposure; paint manufacturing; ventilation standard.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
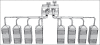




Similar articles
-
Control of workers' exposure to xylene in a pesticide production factory.Int J Occup Environ Health. 2015;21(2):121-6. doi: 10.1179/2049396714Y.0000000098. Epub 2014 Dec 8. Int J Occup Environ Health. 2015. PMID: 25487643 Free PMC article.
-
The challenges of controlling organic solvents in a paint factory due to solvent impurity.Ind Health. 2009 Jul;47(3):326-32. doi: 10.2486/indhealth.47.326. Ind Health. 2009. PMID: 19531919
-
Reduced exposure to organic solvents by use of water-based paint systems in car repair shops.Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2004 Jan;77(1):31-8. doi: 10.1007/s00420-003-0483-0. Epub 2003 Nov 7. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2004. PMID: 14605898
-
Exposure to mixtures of solvents among paint workers and biochemical alterations of liver function.Br J Ind Med. 1991 Oct;48(10):696-701. doi: 10.1136/oem.48.10.696. Br J Ind Med. 1991. PMID: 1931729 Free PMC article.
-
Occupational health hazards and wide spectrum of genetic damage by the organic solvent fumes at the workplace: A critical appraisal.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 May;29(21):30954-30966. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-18889-6. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35102507 Review.
Cited by
-
Biological monitoring of blood naphthalene levels as a marker of occupational exposure to PAHs among auto-mechanics and spray painters in Rawalpindi.BMC Public Health. 2011 Jun 13;11:467. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-11-467. BMC Public Health. 2011. PMID: 21668991 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of environmental and biological monitoring methods for toluene exposure assessment in paint industry.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2023 Feb;30(2):103538. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.103538. Epub 2022 Dec 13. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36590749 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Analysis Characterization of Benzene and Demographic Factors toward Immunoglobulin A.Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2018 Dec 13;6(12):2381-2385. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2018.488. eCollection 2018 Dec 20. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30607197 Free PMC article.
-
Occupational exposure of a medical school staff to formaldehyde in tehran.Tanaffos. 2012;11(3):36-41. Tanaffos. 2012. PMID: 25191427 Free PMC article.
-
Control of workers' exposure to xylene in a pesticide production factory.Int J Occup Environ Health. 2015;21(2):121-6. doi: 10.1179/2049396714Y.0000000098. Epub 2014 Dec 8. Int J Occup Environ Health. 2015. PMID: 25487643 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ridgwaya P, Nixon TE, Leach JP. Occupational exposure to organic solvents and long-term nervous system damage detectable by brain imaging, neurophysiology or histopathology. Food Chem Toxicol. 2003;41:153–87. - PubMed
-
- NIOSH, Occupational Diseases - A Guide to their Recognition, in Publication No 77-181. 1977.
-
- Williams PR, Knutsen JS, Atkinson C, Madl AK, Paustenbach DJ. Airborne concentrations of benzene associated with the historical use of some formulations of liquid wrench. J Occup Environ Hyg. 2007;4(8):547–561. - PubMed
-
- McMinn BW. Control of VOC emissions from ink and paint manufacturing processes. C.T. Center. Environmental Protection Agency. 1992.
-
- ACGIH, Industrial Ventilation a manual of recommended practice. 22 ed. ACGIH; 1995.

