The WD40 domain is required for LRRK2 neurotoxicity
- PMID: 20041156
- PMCID: PMC2794542
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008463
The WD40 domain is required for LRRK2 neurotoxicity
Abstract
Background: Mutations in leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) are the most common genetic cause of Parkinson disease (PD). LRRK2 contains an "enzymatic core" composed of GTPase and kinase domains that is flanked by leucine-rich repeat (LRR) and WD40 protein-protein interaction domains. While kinase activity and GTP-binding have both been implicated in LRRK2 neurotoxicity, the potential role of other LRRK2 domains has not been as extensively explored.
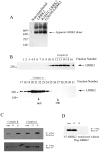
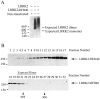
Principal findings: We demonstrate that LRRK2 normally exists in a dimeric complex, and that removing the WD40 domain prevents complex formation and autophosphorylation. Moreover, loss of the WD40 domain completely blocks the neurotoxicity of multiple LRRK2 PD mutations.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that LRRK2 dimerization and autophosphorylation may be required for the neurotoxicity of LRRK2 PD mutations and highlight a potential role for the WD40 domain in the mechanism of LRRK2-mediated cell death.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 binds to neuronal vesicles through protein interactions mediated by its C-terminal WD40 domain.Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Jun;34(12):2147-61. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00914-13. Epub 2014 Mar 31. Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24687852 Free PMC article.
-
Expression, purification and preliminary biochemical and structural characterization of the leucine rich repeat namesake domain of leucine rich repeat kinase 2.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Mar;1824(3):450-60. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2011.12.009. Epub 2012 Jan 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22251894
-
Autophosphorylation in the leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) GTPase domain modifies kinase and GTP-binding activities.J Mol Biol. 2011 Sep 9;412(1):94-110. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.07.033. Epub 2011 Jul 22. J Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21806997 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical and molecular features of LRRK2 and its pathophysiological roles in Parkinson's disease.BMB Rep. 2010 Apr;43(4):233-44. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2010.43.4.233. BMB Rep. 2010. PMID: 20423607 Review.
-
Understanding the GTPase Activity of LRRK2: Regulation, Function, and Neurotoxicity.Adv Neurobiol. 2017;14:71-88. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-49969-7_4. Adv Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 28353279 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The LRRK2 G2385R variant is a partial loss-of-function mutation that affects synaptic vesicle trafficking through altered protein interactions.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 14;7(1):5377. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05760-9. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28710481 Free PMC article.
-
G2385R and I2020T Mutations Increase LRRK2 GTPase Activity.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:7917128. doi: 10.1155/2016/7917128. Epub 2016 May 25. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27314038 Free PMC article.
-
LRRK2, a puzzling protein: insights into Parkinson's disease pathogenesis.Exp Neurol. 2014 Nov;261:206-16. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.05.025. Epub 2014 Jun 4. Exp Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24907399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LRRK2 is involved in the IFN-gamma response and host response to pathogens.J Immunol. 2010 Nov 1;185(9):5577-85. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000548. Epub 2010 Oct 4. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20921534 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling the role of defective genes.Prog Brain Res. 2010;183:43-57. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(10)83003-1. Prog Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20696314 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nussbaum RL, Polymeropoulos MH. Genetics of Parkinson's disease. Hum Mol Genet. 1997;6:1687–1691. - PubMed
-
- de Rijk MC, Tzourio C, Breteler MM, Dartigues JF, Amaducci L, et al. Prevalence of parkinsonism and Parkinson's disease in Europe: the EUROPARKINSON Collaborative Study. European Community Concerted Action on the Epidemiology of Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1997;62:10–15. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Klein C, Lohmann-Hedrich K. Impact of recent genetic findings in Parkinson's disease. Curr Opin Neurol. 2007;20:453–464. - PubMed
-
- Hardy J, Cai H, Cookson MR, Gwinn-Hardy K, Singleton A. Genetics of Parkinson's disease and parkinsonism. Ann Neurol. 2006;60:389–398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

