Common genetic variation and the control of HIV-1 in humans
- PMID: 20041166
- PMCID: PMC2791220
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000791
Common genetic variation and the control of HIV-1 in humans
Abstract
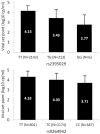
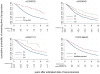
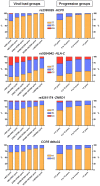
To extend the understanding of host genetic determinants of HIV-1 control, we performed a genome-wide association study in a cohort of 2,554 infected Caucasian subjects. The study was powered to detect common genetic variants explaining down to 1.3% of the variability in viral load at set point. We provide overwhelming confirmation of three associations previously reported in a genome-wide study and show further independent effects of both common and rare variants in the Major Histocompatibility Complex region (MHC). We also examined the polymorphisms reported in previous candidate gene studies and fail to support a role for any variant outside of the MHC or the chemokine receptor cluster on chromosome 3. In addition, we evaluated functional variants, copy-number polymorphisms, epistatic interactions, and biological pathways. This study thus represents a comprehensive assessment of common human genetic variation in HIV-1 control in Caucasians.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Telenti A, Bleiber G. Host genetics of HIV-1 susceptibility. Future Virology. 2006;1:55–70.
-
- O'Brien SJ, Nelson GW. Human genes that limit AIDS. Nat Genet. 2004;36:565–574. - PubMed
-
- Martin MP, Carrington M. Immunogenetics of viral infections. Curr Opin Immunol. 2005;17:510–516. - PubMed
-
- Carrington M, O'Brien SJ. The influence of HLA genotype on AIDS. Annu Rev Med. 2003;54:535–551. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

