Introduction to the quantitative analysis of two-dimensional fluorescence microscopy images for cell-based screening
- PMID: 20041172
- PMCID: PMC2791844
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000603
Introduction to the quantitative analysis of two-dimensional fluorescence microscopy images for cell-based screening
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
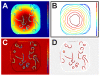
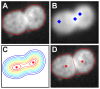
Figures



Similar articles
-
Multispectral microscopy and cell segmentation for analysis of thyroid fine needle aspiration cytology smears.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2009;2009:5645-8. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2009.5333764. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2009. PMID: 19964406
-
A method to unmix multiple fluorophores in microscopy images with minimal a priori information.Opt Express. 2009 Dec 7;17(25):22747-60. doi: 10.1364/OE.17.022747. Opt Express. 2009. PMID: 20052200
-
Non-rigid registration of 3D multi-channel microscopy images of cell nuclei.Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2006;9(Pt 1):907-14. doi: 10.1007/11866565_111. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2006. PMID: 17354977
-
Assessement of rheumatic diseases with computational radiology: current status and future potential.Eur J Radiol. 2009 Aug;71(2):211-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2009.04.046. Epub 2009 May 19. Eur J Radiol. 2009. PMID: 19457632 Review.
-
New opportunities in computer-aided diagnosis: change detection and characterization.J Am Coll Radiol. 2006 Jun;3(6):468-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jacr.2006.03.004. J Am Coll Radiol. 2006. PMID: 17412102 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Shedding light on filovirus infection with high-content imaging.Viruses. 2012 Aug;4(8):1354-71. doi: 10.3390/v4081354. Epub 2012 Aug 23. Viruses. 2012. PMID: 23012631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
STSE: Spatio-Temporal Simulation Environment Dedicated to Biology.BMC Bioinformatics. 2011 Apr 28;12:126. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-126. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 21527030 Free PMC article.
-
Closed-form density-based framework for automatic detection of cellular morphology changes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 May 29;109(22):8382-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1117796109. Epub 2012 May 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22586080 Free PMC article.
-
Image Quality Ranking Method for Microscopy.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 1;6:28962. doi: 10.1038/srep28962. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27364703 Free PMC article.
-
CIDRE: an illumination-correction method for optical microscopy.Nat Methods. 2015 May;12(5):404-6. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3323. Epub 2015 Mar 16. Nat Methods. 2015. PMID: 25775044
References
-
- Sönnichsen B, Koski L, Walsh A, Marschall P, Neumann B, et al. Full-genome RNAi profiling of early embryogenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 2005;434:462–469. - PubMed
-
- Eggert US, Kiger AA, Richter C, Perlman ZE, Perrimon N, et al. Parallel chemical genetic and genome-wide RNAi screens identify cytokinesis inhibitors and targets. PLoS Biology. 2004;2:e379. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0020379. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lockett S, Jacobson K, Herman B. Quantitative precision of an automated, fluorescence-based image cytometer. Anal Quant Cytol Histol. 1992;14:187–202. - PubMed
-
- Boland MV, Murphy RF. A neural network classifier capable of recognizing the patterns of all major subcellular structures in fluorescence microscope images of HeLa cells. Bioinformatics. 2001;17:1213–1223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

