Rational mutational analysis of a multidrug MFS transporter CaMdr1p of Candida albicans by employing a membrane environment based computational approach
- PMID: 20041202
- PMCID: PMC2789324
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000624
Rational mutational analysis of a multidrug MFS transporter CaMdr1p of Candida albicans by employing a membrane environment based computational approach
Abstract
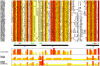
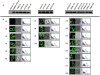
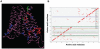
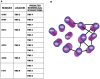
CaMdr1p is a multidrug MFS transporter of pathogenic Candida albicans. An over-expression of the gene encoding this protein is linked to clinically encountered azole resistance. In-depth knowledge of the structure and function of CaMdr1p is necessary for an effective design of modulators or inhibitors of this efflux transporter. Towards this goal, in this study, we have employed a membrane environment based computational approach to predict the functionally critical residues of CaMdr1p. For this, information theoretic scores which are variants of Relative Entropy (Modified Relative Entropy RE(M)) were calculated from Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA) by separately considering distinct physico-chemical properties of transmembrane (TM) and inter-TM regions. The residues of CaMdr1p with high RE(M) which were predicted to be significantly important were subjected to site-directed mutational analysis. Interestingly, heterologous host Saccharomyces cerevisiae, over-expressing these mutant variants of CaMdr1p wherein these high RE(M) residues were replaced by either alanine or leucine, demonstrated increased susceptibility to tested drugs. The hypersensitivity to drugs was supported by abrogated substrate efflux mediated by mutant variant proteins and was not attributed to their poor expression or surface localization. Additionally, by employing a distance plot from a 3D deduced model of CaMdr1p, we could also predict the role of these functionally critical residues in maintaining apparent inter-helical interactions to provide the desired fold for the proper functioning of CaMdr1p. Residues predicted to be critical for function across the family were also found to be vital from other previously published studies, implying its wider application to other membrane protein families.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Prasad R, Kapoor K. Multidrug resistance in yeast Candida. Int Rev Cytol. 2005;242:215–248. - PubMed
-
- Gaur M, Choudhury D, Prasad R. Complete inventory of ABC proteins in human pathogenic yeast, Candida albicans. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2005;9:3–15. - PubMed
-
- Smriti, Krishnamurthy S, Dixit BL, Gupta CM, Milewski S, et al. ABC transporters Cdr1p, Cdr2p and Cdr3p of a human pathogen Candida albicans are general phospholipid translocators. Yeast. 2002;19:303–318. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

