Proliferation and apoptotic rates and increased frequency of p63-positive cells in the prostate acinar epithelium of alloxan-induced diabetic rats
- PMID: 20041964
- PMCID: PMC2965900
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2009.00696.x
Proliferation and apoptotic rates and increased frequency of p63-positive cells in the prostate acinar epithelium of alloxan-induced diabetic rats
Abstract
The effects of experimental type 1 diabetes were investigated in the acinar epithelium of rat ventral prostate, focusing on the rates of cell proliferation and the frequency of apoptosis and p63-positive cells. Type 1 diabetes was induced in adult male Wistar rats by a single alloxan administration (42 mg/kg b.w.) and its effects were analysed for 1 week and 3 months after the establishment of the disease. A group of diabetic rats was treated daily with 5 IU of insulin during 1 week after diabetes had been diagnosed. Immunocytochemical methods for the localization of cell proliferation antigen (PCNA), androgen receptor (AR) and p63 protein were carried out, and apoptotic cells were identified by TUNEL essay. In diabetic rats, testosterone levels reduced drastically after 1 week and in a lower degree after 3 months. In short-term diabetic rats, cell proliferation decreased, and in medium-term, epithelial apoptotic rates increased. In both periods after the onset of diabetes, the frequency of p63-positive cells doubled. Insulin treatment was effective in preventing testosterone decrease, p63-positive cell increase and apoptotic rates, but did not interfere in cell proliferation. This investigation shows that, soon after diabetes onset, there are important modifications in cell proliferation within the acinar prostatic epithelium, and in longer term, there is a marked impact on kinetics of differentiation and cell death, which may initially be attributable to an androgenic fall, but is probably also because of other factors related to diabetes, as changes are considerably different from those resulting from castration.
Figures

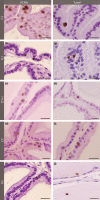
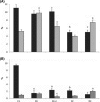
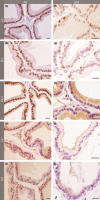
References
-
- Andreoni GI, Veneziano DB, Giannotti-Filho O, Marigo C, Mirra AP, Fonseca LAM. Cancer incidence in eighteen cities of the State of São Paulo, Brazil Incidência de câncer em dezoito cidades do Estado de São Paulo. Rev. Saúde Pública. 2001;35:362–367. - PubMed
-
- Antonioli E. 77f Modulação hormonal do comportamento das células musculares lisas prostáticas in vitro e in vivoDissertação (Mestrado) Campinas: Instituto de Biologia- Universidade Estadual de Campinas; 2003.
-
- Blanchere M, Mestayer C, Saunier E, Broshuis M. Transforming growth factor B in the human prostate: its role in stromal-epithelial interactions in non-cancerous cell culture. Prostate. 2001;46:311–318. - PubMed
-
- Bonkhoff H. Role of the basal cells in premalignant changes of the human prostate: a stem cell concept for the development of prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 1996;30:201–205. - PubMed
-
- Bonkhoff H, Remberger K. Differentiation pathways and histogenetic aspects of normal and abnormal prostatic growth: a stem cell model. Prostate. 1996;28:98–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

