Altered expression of claudin family proteins in Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia brains
- PMID: 20041969
- PMCID: PMC3822746
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00999.x
Altered expression of claudin family proteins in Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia brains
Abstract
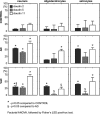
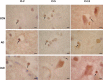
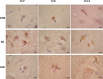
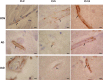
Claudins (Cls) are a multigene family of transmembrane proteins with different tissue distribution, which have an essential role in the formation and sealing capacity of tight junctions (TJs). At the level of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), TJs are the main molecular structures which separate the neuronal milieu from the circulatory space, by a restriction of the paracellular flow of water, ions and larger molecules into the brain. Different studies suggested recently significant BBB alterations in both vascular and degenerative dementia types. In a previous study we found in Alzheimer's disease (AD) and vascular dementia (VaD) brains an altered expression of occludin, a molecular partner of Cls in the TJs structure. Therefore in this study, using an immunohistochemical approach, we investigated the expression of Cl family proteins (Cl-2, Cl-5 and Cl-11) in frontal cortex of aged control, AD and VaD brains. To estimate the number of Cl-expressing cells, we applied a random systematic sampling and the unbiased optical fractionator method. We found selected neurons, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes and endothelial cells expressing Cl-2, Cl-5 and Cl-11 at detectable levels in all cases studied. We report a significant increase in ratio of neurons expressing Cl-2, Cl-5 and Cl-11 in both AD and VaD as compared to aged controls. The ratio of astrocytes expressing Cl-2 and Cl-11 was significantly higher in AD and VaD as compared to aged controls. The ratio of oligodendrocytes expressing Cl-11 was significantly higher in AD and the ratio of oligodendrocytes expressing Cl-2 was significantly higher in VaD as compared to aged controls. Within the cerebral cortex, Cls were selectively expressed by pyramidal neurons, which are the ones responsible for cognitive processes and affected by AD pathology. Our findings suggest a new function of Cl family proteins which might be linked to response to cellular stress.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Occludin is overexpressed in Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia.J Cell Mol Med. 2007 May-Jun;11(3):569-79. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00047.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2007. PMID: 17635647 Free PMC article.
-
Claudin expression profile separates Alzheimer's disease cases from normal aging and from vascular dementia cases.J Neurol Sci. 2012 Nov 15;322(1-2):184-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2012.05.031. Epub 2012 Jun 3. J Neurol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22664153
-
Loss of capillary pericytes and the blood-brain barrier in white matter in poststroke and vascular dementias and Alzheimer's disease.Brain Pathol. 2020 Nov;30(6):1087-1101. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12888. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Brain Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32705757 Free PMC article.
-
Rhizoma Coptidis for Alzheimer's Disease and Vascular Dementia: A Literature Review.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2020;18(4):358-368. doi: 10.2174/1570161117666190710151545. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31291876 Review.
-
Dysregulation of Ion Channels and Transporters and Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease and Vascular Dementia.Aging Dis. 2024 Aug 1;15(4):1748-1770. doi: 10.14336/AD.2023.1201. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 38300642 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Selective loss of cortical endothelial tight junction proteins during Alzheimer's disease progression.Brain. 2019 Apr 1;142(4):1077-1092. doi: 10.1093/brain/awz011. Brain. 2019. PMID: 30770921 Free PMC article.
-
Differential display RT-PCR reveals genes associated with lithium-induced neuritogenesis in SK-N-MC cells.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2011 Oct;31(7):1021-6. doi: 10.1007/s10571-011-9699-9. Epub 2011 May 6. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21547488 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-specific genetic predictors of Alzheimer's disease biomarkers.Acta Neuropathol. 2018 Dec;136(6):857-872. doi: 10.1007/s00401-018-1881-4. Epub 2018 Jul 2. Acta Neuropathol. 2018. PMID: 29967939 Free PMC article.
-
Host Akkermansia muciniphila Abundance Correlates With Gulf War Illness Symptom Persistence via NLRP3-Mediated Neuroinflammation and Decreased Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor.Neurosci Insights. 2020 Jul 27;15:2633105520942480. doi: 10.1177/2633105520942480. eCollection 2020. Neurosci Insights. 2020. PMID: 32832901 Free PMC article.
-
Neurovascular unit in chronic pain.Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:648268. doi: 10.1155/2013/648268. Epub 2013 Jun 5. Mediators Inflamm. 2013. PMID: 23840097 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Popescu BO, Toescu EC, Popescu LM, et al. Blood-brain barrier alterations in ageing and dementia. J Neurol Sci. 2009;283:99–106. - PubMed
-
- Schneeberger EE, Lynch RD. The tight junction: a multifunctional complex. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004;286:C1213–28. - PubMed
-
- Rubin LL. The blood-brain barrier in and out of cell culture. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1991;1:360–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

