The chemokine CXCL13 is a key regulator of B cell recruitment to the cerebrospinal fluid in acute Lyme neuroborreliosis
- PMID: 20042073
- PMCID: PMC2811704
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-6-42
The chemokine CXCL13 is a key regulator of B cell recruitment to the cerebrospinal fluid in acute Lyme neuroborreliosis
Abstract
Background: The chemokine CXCL13 is known to dictate homing and motility of B cells in lymphoid tissue and has been implicated in the formation of ectopic lymphoid tissue in chronic inflammation. Whether it influences B cell trafficking during acute infection, is largely unclear. In previous studies, we showed that (I) CXCL13 levels are markedly increased in the B cell-rich cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of patients with acute Lyme neuroborreliosis (LNB), and (II) CXCL13 is released by monocytes upon recognition of borrelial outer surface proteins by Toll-like receptor 2. Here, we assessed the role of CXCL13--in comparison to other chemokines--in the recruitment of B cells to the CSF of patients with acute LNB.
Methods: Measurement of chemokines was done by ELISA. B cells were isolated from whole blood using magnetic cell separation (MACS). For migration experiments, a modified Boyden chamber assay was used and the migrated B cells were further analysed by FACS. The migration was inhibited either by preincubation of the CSF samples with neutralizing antibodies, heating to 60 degrees C, removal of proteins >3 kDa, or by pre-treatment of the B cells with pertussis toxin. The principal statistical tests used were one-way analysis of variance and Bonferroni test (chemokine measurements) as well as paired Student's t-test (migration experiments).
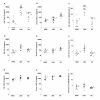
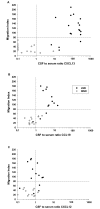
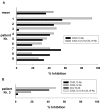
Results: Measurements of chemokine levels revealed an increase in three of the four known major B cell chemoattractants CXCL13, CCL19 and CXCL12 in LNB CSF. The CXCL13 CSF:serum ratio, as a measure of the chemotactic gradient, was substantially higher than that of CCL19 and CXCL12. Moreover, the chemotactic activity of LNB CSF was reduced up to 56% after preincubation with a neutralizing CXCL13 antibody, while combined preincubation with antibodies against CXCL13, CCL19, and CXCL12 did not lead to further reduction. Since treatment with pertussis toxin, heating to 60 degrees C, and removal of proteins >3 kDa abrogated the chemotactic activity, further not yet identified chemokines seem to be involved in B cell recruitment to LNB CSF.
Conclusion: Combined, our study suggests a key role of CXCL13 in B cell migration to sites of infection as shown here for the CSF of LNB patients.
Figures
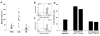

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

