A genomic glimpse of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases in malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum
- PMID: 20042123
- PMCID: PMC2813244
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-644
A genomic glimpse of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases in malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum
Abstract
Background: Plasmodium parasites are causative agents of malaria which affects >500 million people and claims approximately 2 million lives annually. The completion of Plasmodium genome sequencing and availability of PlasmoDB database has provided a platform for systematic study of parasite genome. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (aaRSs) are pivotal enzymes for protein translation and other vital cellular processes. We report an extensive analysis of the Plasmodium falciparum genome to identify and classify aaRSs in this organism.
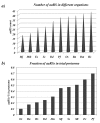
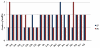
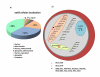
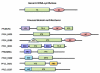
Results: Using various computational and bioinformatics tools, we have identified 37 aaRSs in P. falciparum. Our key observations are: (i) fraction of proteome dedicated to aaRSs in P. falciparum is very high compared to many other organisms; (ii) 23 out of 37 Pf-aaRS sequences contain signal peptides possibly directing them to different cellular organelles; (iii) expression profiles of Pf-aaRSs vary considerably at various life cycle stages of the parasite; (iv) several PfaaRSs posses very unusual domain architectures; (v) phylogenetic analyses reveal evolutionary relatedness of several parasite aaRSs to bacterial and plants aaRSs; (vi) three dimensional structural modelling has provided insights which could be exploited in inhibitor discovery against parasite aaRSs.
Conclusion: We have identified 37 Pf-aaRSs based on our bioinformatics analysis. Our data reveal several unique attributes in this protein family. We have annotated all 37 Pf-aaRSs based on predicted localization, phylogenetics, domain architectures and their overall protein expression profiles. The sets of distinct features elaborated in this work will provide a platform for experimental dissection of this family of enzymes, possibly for the discovery of novel drugs against malaria.
Figures


References
-
- Burbaum JJ, Schimmel P. Structural relationships and the classification of aminoacyl- tRNA synthetases. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:16965–16968. - PubMed
-
- Wolf YI, Aravind L, Grishin NV, Koonin EV. Evolution of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases-analysis of unique domain architectures and phylogenetic trees reveals a complex history of horizontal gene transfer events. Genome Res. . 1999;9(8):689–710. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

