Emerging synergy between nanotechnology and implantable biosensors: a review
- PMID: 20042326
- PMCID: PMC2846767
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2009.12.001
Emerging synergy between nanotechnology and implantable biosensors: a review
Abstract
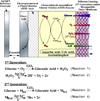
The development of implantable biosensors for continuous monitoring of metabolites is an area of sustained scientific and technological interests. On the other hand, nanotechnology, a discipline which deals with the properties of materials at the nanoscale, is developing as a potent tool to enhance the performance of these biosensors. This article reviews the current state of implantable biosensors, highlighting the synergy between nanotechnology and sensor performance. Emphasis is placed on the electrochemical method of detection in light of its widespread usage and substantial nanotechnology based improvements in various aspects of electrochemical biosensor performance. Finally, issues regarding toxicity and biocompatibility of nanomaterials, along with future prospects for the application of nanotechnology in implantable biosensors, are discussed.
(c) 2009 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
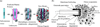
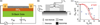



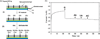
Similar articles
-
Biosensors for real-time in vivo measurements.Biosens Bioelectron. 2005 Jun 15;20(12):2388-403. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2004.12.003. Epub 2005 Jan 15. Biosens Bioelectron. 2005. PMID: 15854814 Review.
-
Ion sensitive field effect transducer-based biosensors.Biotechnol Adv. 2003 Sep;21(6):527-34. doi: 10.1016/s0734-9750(03)00103-4. Biotechnol Adv. 2003. PMID: 14499153 Review.
-
Nanotechnology for implantable sensors: carbon nanotubes and graphene in medicine.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2013 May-Jun;5(3):233-49. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1213. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23450525 Review.
-
Recent advances in nanomaterial-based biosensors for antibiotics detection.Biosens Bioelectron. 2017 May 15;91:504-514. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2017.01.007. Epub 2017 Jan 5. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017. PMID: 28082239 Review.
-
Biosensing: new probes offer much faster results.Nat Nanotechnol. 2007 Dec;2(12):746-8. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2007.398. Nat Nanotechnol. 2007. PMID: 18654424 No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Skin-Integrated Wearable Systems and Implantable Biosensors: A Comprehensive Review.Biosensors (Basel). 2020 Jul 21;10(7):79. doi: 10.3390/bios10070079. Biosensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32708103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating the clinical accuracy of GlucoMen®Day: a novel microdialysis-based continuous glucose monitor.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2010 Sep 1;4(5):1182-92. doi: 10.1177/193229681000400517. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2010. PMID: 20920438 Free PMC article.
-
Microspheres prepared with PLGA blends for delivery of dexamethasone for implantable medical devices.Pharm Res. 2014 Feb;31(2):373-81. doi: 10.1007/s11095-013-1166-5. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Pharm Res. 2014. PMID: 23949251
-
Biomechanics of the sensor-tissue interface-effects of motion, pressure, and design on sensor performance and the foreign body response-part I: theoretical framework.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2011 May 1;5(3):632-46. doi: 10.1177/193229681100500317. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2011. PMID: 21722578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Progress in Biomedical Sensors Based on Conducting Polymer Hydrogels.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2023 May 15;6(5):1720-1741. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.3c00139. Epub 2023 Apr 28. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2023. PMID: 37115912 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abidian MR, Martin DC. Adv. Func. Mat. 2009;19(4):573–585.
-
- Adiga SP, Curtiss LA, Elam JW, Pellin MJ, Shih CC, Shih CM, Lin SJ, Su YY, Gittard SD, Zhang J, Narayan RJ. J. Minerals, Met. Materials Soc. 2008;60(3):26–32.
-
- Ainslie KM, Sharma G, Dyer MA, Grimes CA, Pishko MV. Nano Lett. 2005;5(9):1852–1856. - PubMed
-
- Ainslie KM, Tao SL, Popat KC, Desai TA. ACS Nano. 2008;2(5):1076–1084. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

