Pseudotyping incompatibility between HIV-1 and gibbon ape leukemia virus Env is modulated by Vpu
- PMID: 20042505
- PMCID: PMC2826068
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01562-09
Pseudotyping incompatibility between HIV-1 and gibbon ape leukemia virus Env is modulated by Vpu
Abstract
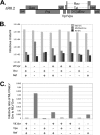
The Env protein from gibbon ape leukemia virus (GaLV) has been shown to be incompatible with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) in the production of infectious pseudotyped particles. This incompatibility has been mapped to the C-terminal cytoplasmic tail of GaLV Env. Surprisingly, we found that the HIV-1 accessory protein Vpu modulates this incompatibility. The infectivity of HIV-1 pseudotyped with murine leukemia virus (MLV) Env was not affected by Vpu. However, the infectivity of HIV-1 pseudotyped with an MLV Env with the cytoplasmic tail from GaLV Env (MLV/GaLV Env) was restricted 50- to 100-fold by Vpu. A Vpu mutant containing a scrambled membrane-spanning domain, Vpu(RD), was still able to restrict MLV/GaLV Env, but mutation of the serine residues at positions 52 and 56 completely alleviated the restriction. Loss of infectivity appeared to be caused by reduced MLV/GaLV Env incorporation into viral particles. The mechanism of this downmodulation appears to be distinct from Vpu-mediated CD4 downmodulation because Vpu-expressing cells that failed to produce infectious HIV-1 particles nonetheless continued to display robust surface MLV/GaLV Env expression. In addition, if MLV and HIV-1 were simultaneously introduced into the same cells, only the HIV-1 particle infectivity was restricted by Vpu. Collectively, these data suggest that Vpu modulates the cellular distribution of MLV/GaLV Env, preventing its recruitment to HIV-1 budding sites.
Figures





References
-
- Beard, B. C., P. Mezquita, J. C. Morris, and H. P. Kiem. 2006. Efficient transduction and engraftment of G-CSF-mobilized peripheral blood CD34+ cells in nonhuman primates using GALV-pseudotyped gammaretroviral vectors. Mol. Ther. 14:212-217. - PubMed
-
- Chesebro, B., K. Wehrly, J. Nishio, and S. Perryman. 1992. Macrophage-tropic human immunodeficiency virus isolates from different patients exhibit unusual V3 envelope sequence homogeneity in comparison with T-cell-tropic isolates: definition of critical amino acids involved in cell tropism. J. Virol. 66:6547-6554. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

