High seroprevalence of neutralizing capacity against human metapneumovirus in all age groups studied in Bonn, Germany
- PMID: 20042516
- PMCID: PMC2837972
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00398-09
High seroprevalence of neutralizing capacity against human metapneumovirus in all age groups studied in Bonn, Germany
Abstract
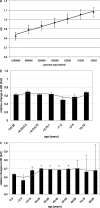
Human metapneumovirus (hMPV) infections occur frequently despite high rates of perpetual seroprevalence for all age groups. Analyses of approximately 2,000 archived, randomly selected serum samples demonstrated that neutralizing capacities remain high, with a minor decrease for individuals over 69 years of age, leading to the hypothesis that reinfections occur because humoral immune responses play minor roles in the clearance of hMPV infections.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RSV and HMPV seroprevalence in Tuscany (Italy) and North-Rhine Westfalia (Germany) in the winter season 2009/2010.Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2011 Nov;5(6):380-1. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-2659.2011.00252.x. Epub 2011 Apr 18. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2011. PMID: 21668674 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Seroprevalence of human respiratory syncytial virus and human metapneumovirus in healthy population analyzed by recombinant fusion protein-based enzyme linked immunosorbent assay.Virol J. 2012 Jul 2;9:130. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-9-130. Virol J. 2012. PMID: 22748150 Free PMC article.
-
[Analysis of neutralizing activity of sera from 0 to 6 years old children in Chongqing area against human metapneumovirus].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2007 Jun;45(6):432-6. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2007. PMID: 17880789 Chinese.
-
Human Metapneumovirus.Microbiol Spectr. 2014 Oct;2(5). doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.AID-0020-2014. Microbiol Spectr. 2014. PMID: 26104361 Review.
-
Human metapneumovirus: a newly emerging respiratory pathogen.Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2003 Jun;16(3):255-8. doi: 10.1097/00001432-200306000-00012. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2003. PMID: 12821817 Review.
Cited by
-
Human Metapneumovirus: lessons learned over the first decade.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011 Oct;24(4):734-54. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00015-11. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21976607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical and Radiologic Characteristics of Human Metapneumovirus Infections in Adults, South Korea.Emerg Infect Dis. 2019 Jan;25(1):15-24. doi: 10.3201/eid2501.181131. Emerg Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30560776 Free PMC article.
-
Immunologic Profiling of Human Metapneumovirus for the Development of Targeted Immunotherapy.J Infect Dis. 2017 Sep 15;216(6):678-687. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix358. J Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28934427 Free PMC article.
-
Lung CD8+ T Cell Impairment Occurs during Human Metapneumovirus Infection despite Virus-Like Particle Induction of Functional CD8+ T Cells.J Virol. 2015 Sep;89(17):8713-26. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00670-15. Epub 2015 Jun 10. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26063431 Free PMC article.
-
A Re-emerging Respiratory Virus: Human Metapneumovirus (hMPV).Cureus. 2025 Feb 1;17(2):e78354. doi: 10.7759/cureus.78354. eCollection 2025 Feb. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40034641 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boivin, G., Y. Abed, G. Pelletier, L. Ruel, D. Moisan, S. Cote, T. C. Peret, D. D. Erdman, and L. J. Anderson. 2002. Virological features and clinical manifestations associated with human metapneumovirus: a new paramyxovirus responsible for acute respiratory-tract infections in all age groups. J. Infect. Dis. 186:1330-1334. - PubMed
-
- Boivin, G., S. G. De, M. E. Hamelin, S. Cote, M. Argouin, G. Tremblay, R. Maranda-Aubut, C. Sauvageau, M. Ouakki, N. Boulianne, and C. Couture. 2007. An outbreak of severe respiratory tract infection due to human metapneumovirus in a long-term care facility. Clin. Infect. Dis. 44:1152-1158. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

