SHP-1 deficient mast cells are hyperresponsive to stimulation and critical in initiating allergic inflammation in the lung
- PMID: 20042576
- PMCID: PMC4755278
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901972
SHP-1 deficient mast cells are hyperresponsive to stimulation and critical in initiating allergic inflammation in the lung
Abstract
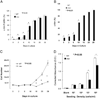
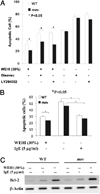
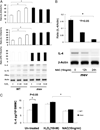
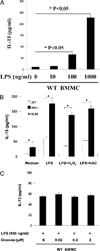
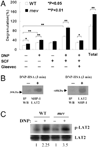
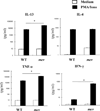
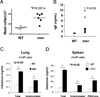
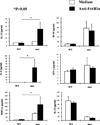
Phosphatase Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase 1 (SHP-1)-deficient mice display an allergic asthma phenotype that is largely IL-13 and STAT6 dependent. The cell types responsible for the Th2 phenotype have not been identified. We hypothesized that SHP-1 deficiency leads to mast cell dysregulation and increased production and release of mediators and Th2 cytokines, leading to the allergic asthma phenotype. We examined SHP-1 regulation of mast cell differentiation, survival, and functional responses to stimulation using bone marrow-derived mast cells from viable motheaten (mev) mice. We assessed pulmonary phenotypical changes in mev mice on the mast cell-deficient Kit(W-Sh) genetic background. The results showed that SHP-1 deficiency led to increased differentiation and survival, but reduced proliferation, of mast cells. SHP-1-deficient mast cells produced and released increased amounts of mediators and Th2 cytokines IL-4 and -13 spontaneously and in response to H(2)O(2), LPS, and Fc epsilonI cross-linking, involving c-Kit-dependent and -independent processes. The Fc epsilonRI signaling led to binding of SHP-1 to linker for activation of T cells 2 and enhanced linker for activation of T cells 2 phosphorylation in mev bone marrow-derived mast cells. Furthermore, the number of mast cells in the lung tissue of mev mice was increased and mast cell production and release of Th2 cytokines were distinctly increased upon Fc epsilonRI stimulation. When backcrossed to the Kit(W-Sh) background, mev mice had markedly reduced pulmonary inflammation and Th2 cytokine production. These findings demonstrate that SHP-1 is a critical regulator of mast cell development and function and that SHP-1-deficient mast cells are able to produce increased Th2 cytokines and initiate allergic inflammatory responses in the lung.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Moorman JE, Rudd RA, Johnson CA, King M, Minor P, Bailey C, Scalia MR, Akinbami LJ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) National surveillance for asthma—United States, 1980–2004. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2007;56:1–54. - PubMed
-
- Gavett SH, Chen X, Finkelman F, Wills-Karp M. Depletion of murine CD4+ T lymphocytes prevents antigen-induced airway hyperreactivity and pulmonary eosinophilia. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1994;10:587–593. - PubMed
-
- Garlisi CG, Falcone A, Kung TT, Stelts D, Pennline KJ, Beavis AJ, Smith SR, Egan RW, Umland SP. T cells are necessary for Th2 cytokine production and eosinophil accumulation in airways of antigen-challenged allergic mice. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1995;75:75–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

