Formation of a mast cell synapse: Fc epsilon RI membrane dynamics upon binding mobile or immobilized ligands on surfaces
- PMID: 20042583
- PMCID: PMC3087819
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903071
Formation of a mast cell synapse: Fc epsilon RI membrane dynamics upon binding mobile or immobilized ligands on surfaces
Abstract
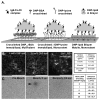
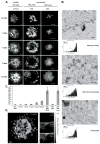
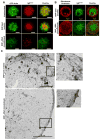
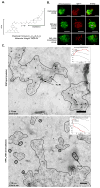
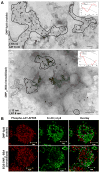
Fc epsilonRI on mast cells form a synapse when presented with mobile, bilayer-incorporated Ag. In this study, we show that receptor reorganization within the contacting mast cell membrane is markedly different upon binding of mobile and immobilized ligands. Rat basophilic leukemia mast cells primed with fluorescent anti-DNP IgE were engaged by surfaces presenting either bilayer-incorporated, monovalent DNP-lipid (mobile ligand), or chemically cross-linked, multivalent DNP (immobilized ligand). Total internal reflection fluorescence imaging and electron microscopy methods were used to visualize receptor reorganization at the contact site. The spatial relationships of Fc epsilonRI to other cellular components at the synapse, such as actin, cholesterol, and linker for activation of T cells, were also analyzed. Stimulation of mast cells with immobilized polyvalent ligand resulted in typical levels of degranulation. Remarkably, degranulation also followed interaction of mast cells, with bilayers presenting mobile, monovalent ligand. Receptors engaged with mobile ligand coalesce into large, cholesterol-rich clusters that occupy the central portion of the contacting membrane. These data indicate that Fc epsilonRI cross-linking is not an obligatory step in triggering mast cell signaling and suggest that dense populations of mobile receptors are capable of initiating low-level degranulation upon ligand recognition.
Figures
References
-
- Oliver JM, Pfeiffer JR, Surviladze Z, Steinberg SL, Leiderman K, Sanders ML, Wofsy C, Zhang J, Fan H, Andrews N, Bunge S, Boyle TJ, Kotula P, Wilson BS. Membrane receptor mapping: the membrane topography of Fc(epsilon)RI signaling. Subcell Biochem. 2004;37:3–34. - PubMed
-
- Sada K, Zhang J, Siraganian RP. SH2 domain-mediated targeting, but not localization, of Syk in the plasma membrane is critical for FcepsilonRI signaling. Blood. 2001;97:1352–1359. - PubMed
-
- Zhang J, Billingsley ML, Kincaid RL, Siraganian RP. Phosphorylation of Syk activation loop tyrosines is essential for Syk function. An in vivo study using a specific anti-Syk activation loop phosphotyrosine antibody. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:35442–35447. - PubMed
-
- Oliver JM, Burg DL, Wilson BS, McLaughlin JL, Geahlen RL. Inhibition of mast cell Fc epsilon R1-mediated signaling and effector function by the Syk-selective inhibitor, piceatannol. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:29697–29703. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

