Cell type-specific recognition of human metapneumoviruses (HMPVs) by retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I) and TLR7 and viral interference of RIG-I ligand recognition by HMPV-B1 phosphoprotein
- PMID: 20042593
- PMCID: PMC2834787
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902750
Cell type-specific recognition of human metapneumoviruses (HMPVs) by retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I) and TLR7 and viral interference of RIG-I ligand recognition by HMPV-B1 phosphoprotein
Abstract
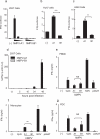
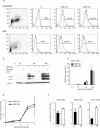
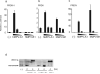
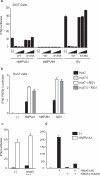
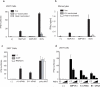
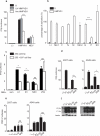
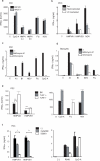
Human metapneumoviruses (HMPVs) are recently identified Paramyxoviridae that contribute to respiratory tract infections in children. No effective treatments or vaccines are available. Successful defense against virus infection relies on early detection by germ line-encoded pattern recognition receptors and activation of cytokine and type I IFN genes. Recently, the RNA helicase retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I) has been shown to sense HMPV. In this study, we investigated the abilities of two prototype strains of HMPV (A1 [NL\1\00] and B1 [NL\1\99]) to activate RIG-I and induce type I IFNs. Despite the abilities of both HMPV-A1 and HMPV-B1 to infect and replicate in cell lines and primary cells, only the HMPV-A1 strain triggered RIG-I to induce IFNA/B gene transcription. The failure of the HMPV-B1 strain to elicit type I IFN production was dependent on the B1 phosphoprotein, which specifically prevented RIG-I-mediated sensing of HMPV viral 5' triphosphate RNA. In contrast to most cell types, plasmacytoid dendritic cells displayed a unique ability to sense both HMPV-A1 and HMPV-B1 and in this case sensing was via TLR7 rather than RIG-I. Collectively, these data reveal differential mechanisms of sensing for two closely related viruses, which operate in cell type-specific manners.
Figures
Similar articles
-
N6-methyladenosine modification enables viral RNA to escape recognition by RNA sensor RIG-I.Nat Microbiol. 2020 Apr;5(4):584-598. doi: 10.1038/s41564-019-0653-9. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Nat Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32015498 Free PMC article.
-
Role of retinoic acid inducible gene-I in human metapneumovirus-induced cellular signalling.J Gen Virol. 2008 Aug;89(Pt 8):1978-1986. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.2008/000778-0. J Gen Virol. 2008. PMID: 18632970 Free PMC article.
-
Human metapneumovirus M2-2 protein inhibits RIG-I signaling by preventing TRIM25-mediated RIG-I ubiquitination.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 15;13:970750. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.970750. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36045682 Free PMC article.
-
Human Metapneumovirus: Mechanisms and Molecular Targets Used by the Virus to Avoid the Immune System.Front Immunol. 2018 Oct 24;9:2466. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02466. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30405642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What Really Rigs Up RIG-I?J Innate Immun. 2016;8(5):429-36. doi: 10.1159/000447947. Epub 2016 Jul 21. J Innate Immun. 2016. PMID: 27438016 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Avian Metapneumovirus Subgroup C Phosphoprotein Suppresses Type I Interferon Production by Blocking Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 Nuclear Translocation.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 14;11(1):e0341322. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03413-22. Epub 2022 Dec 20. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36537793 Free PMC article.
-
Human metapneumovirus - what we know now.F1000Res. 2018 Feb 1;7:135. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.12625.1. eCollection 2018. F1000Res. 2018. PMID: 29744035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Burden of Human Metapneumovirus and Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infections in Hospitalized Norwegian Children.J Infect Dis. 2017 Jul 1;216(1):110-116. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix262. J Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28838133 Free PMC article.
-
Human metapneumovirus glycoprotein G inhibits TLR4-dependent signaling in monocyte-derived dendritic cells.J Immunol. 2011 Jul 1;187(1):47-54. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002589. Epub 2011 Jun 1. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21632720 Free PMC article.
-
Human metapneumovirus M2-2 protein inhibits innate cellular signaling by targeting MAVS.J Virol. 2012 Dec;86(23):13049-61. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01248-12. Epub 2012 Sep 26. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 23015697 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ji W, Chen ZR, Wang YQ. [Comparison of the clinical manifestation and lung function between RSV and hMPV lower respiratory tract infection]. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2009;47:71–73. - PubMed
-
- van den Hoogen BG, Bestebroer TM, Osterhaus AD, Fouchier RA. Analysis of the genomic sequence of a human metapneumovirus. Virology. 2002;295:119–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

