Differentiation of embryonic stem cells 1 (Dies1) is a component of bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4) signaling pathway required for proper differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 20042595
- PMCID: PMC2844221
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.077156
Differentiation of embryonic stem cells 1 (Dies1) is a component of bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4) signaling pathway required for proper differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells
Abstract
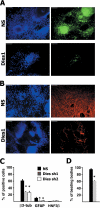
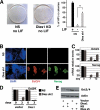
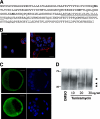
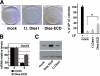
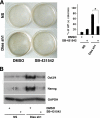
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are pluripotent cells able to grow indefinitely in culture and to differentiate into all cell types of embryos upon specific stimuli. Molecular mechanisms controlling the unique characteristics of ESCs are still largely unknown. We identified Dies1 (Differentiation of ESCs 1), an unpublished gene, that encodes a type I membrane protein. ESCs stably transfected with Dies1 small hairpin RNAs failed to properly differentiate toward neural and cardiac cell fate upon appropriate stimuli and continued to express markers of undifferentiated cells, such as the membrane-associated alkaline phosphatase, and transcription factors, like Oct3/4 and Nanog, when grown under conditions promoting differentiation. Our results demonstrated that Dies1 is required for BMP4/Smad1 signaling cascade; in undifferentiated ESCs Dies1 knockdown did not affect the expression of leukemia inhibitory factor downstream targets, whereas it resulted in a strong decrease of BMP4 signaling, as demonstrated by the decrease of Id1, -2, and -3 mRNAs, the decreased activity of Id1 gene promoter, and the reduced phospho-Smad1 levels. Dies1 knockdown had no effect in murine ESCs when the expression of the BMP4 receptor Alk3 was suppressed. The phenotype induced by Dies1 suppression in ESCs is due to the indirect activation of the Nodal/Activin pathway, which is a consequence of the BMP4 pathway inhibition and is sufficient to support the mESC undifferentiated state in the absence of leukemia inhibitory factor.
Figures
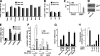
References
-
- Boiani M., Schöler H. R. (2005) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6, 872–884 - PubMed
-
- Niwa H. (2007) Development 134, 635–646 - PubMed
-
- Loh Y. H., Wu Q., Chew J. L., Vega V. B., Zhang W., Chen X., Bourque G., George J., Leong B., Liu J., Wong K. Y., Sung K. W., Lee C. W., Zhao X. D., Chiu K. P., Lipovich L., Kuznetsov V. A., Robson P., Stanton L. W., Wei C. L., Ruan Y., Lim B., Ng H. H. (2006) Nat. Genet. 38, 431–440 - PubMed
-
- Smith A. G., Heath J. K., Donaldson D. D., Wong G. G., Moreau J., Stahl M., Rogers D. (1988) Nature 336, 688–690 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

