SIRT1 suppresses activator protein-1 transcriptional activity and cyclooxygenase-2 expression in macrophages
- PMID: 20042607
- PMCID: PMC2844159
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.038604
SIRT1 suppresses activator protein-1 transcriptional activity and cyclooxygenase-2 expression in macrophages
Abstract
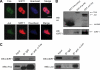
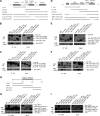
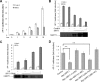
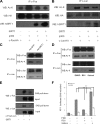
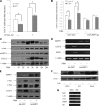
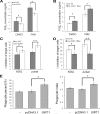
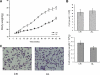
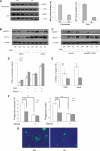
SIRT1 (Sirtuin type 1), a mammalian orthologue of yeast SIR2 (silent information regulator 2), has been shown to mediate a variety of calorie restriction (CR)-induced physiological events, such as cell fate regulation via deacetylation of the substrate proteins. However, whether SIRT1 deacetylates activator protein-1 (AP-1) to influence its transcriptional activity and target gene expression is still unknown. Here we demonstrate that SIRT1 directly interacts with the basic leucine zipper domains of c-Fos and c-Jun, the major components of AP-1, by which SIRT1 suppressed the transcriptional activity of AP-1. This process requires the deacetylase activity of SIRT1. Notably, SIRT1 reduced the expression of COX-2, a typical AP-1 target gene, and decreased prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)) production of peritoneal macrophages (pMPhis). pMPhis with SIRT1 overexpression displayed improved phagocytosis and tumoricidal functions, which are associated with depressed PGE(2). Furthermore, SIRT1 protein level was up-regulated in CR mouse pMPhis, whereas elevated SIRT1 decreased COX-2 expression and improved PGE(2)-related macrophage functions that were reversed following inhibition of SIRT1 deacetylase activity. Thus, our results indicate that SIRT1 may be a mediator of CR-induced macrophage regulation, and its deacetylase activity contributes to the inhibition of AP-1 transcriptional activity and COX-2 expression leading to amelioration of macrophage function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sirt1 suppresses MCP-1 production during the intervertebral disc degeneration by inactivating AP-1 subunits c-Fos/c-Jun.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Jun;24(11):5895-5904. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202006_21482. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32572902
-
Sirtuin 1 is a negative regulator of parathyroid hormone stimulation of matrix metalloproteinase 13 expression in osteoblastic cells: role of sirtuin 1 in the action of PTH on osteoblasts.J Biol Chem. 2015 Mar 27;290(13):8373-82. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.602763. Epub 2015 Jan 28. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25631045 Free PMC article.
-
B-ATF functions as a negative regulator of AP-1 mediated transcription and blocks cellular transformation by Ras and Fos.Oncogene. 2000 Mar 30;19(14):1752-63. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203491. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 10777209
-
Encounters with Fos and Jun on the road to AP-1.Semin Cancer Biol. 1990 Feb;1(1):19-26. Semin Cancer Biol. 1990. PMID: 2133107 Review.
-
Close encounters of many kinds: Fos-Jun interactions that mediate transcription regulatory specificity.Oncogene. 2001 Apr 30;20(19):2438-52. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204385. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11402339 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Sirtuin-1 in Immune Response and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 26;12:632383. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.632383. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33981300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sirtuin 1 regulates hepatitis B virus transcription and replication by targeting transcription factor AP-1.J Virol. 2014 Mar;88(5):2442-51. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02861-13. Epub 2013 Dec 11. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24335313 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT1: A Potential Therapeutic Target in Autoimmune Diseases.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 23;12:779177. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.779177. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34887866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SIRT1 promoter polymorphisms as clinical modifiers on systemic lupus erythematosus.Mol Biol Rep. 2014 Jul;41(7):4233-9. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3294-3. Epub 2014 Feb 26. Mol Biol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24570024
-
PM2.5 Upregulates MicroRNA-146a-3p and Induces M1 Polarization in RAW264.7 Cells by Targeting Sirtuin1.Int J Med Sci. 2019 Jan 29;16(3):384-393. doi: 10.7150/ijms.30084. eCollection 2019. Int J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30911272 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eferl R., Wagner E. F. (2003) Nat. Rev. Cancer 3, 859–868 - PubMed
-
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. (1987) Cell 49, 729–739 - PubMed
-
- Lee S. K., Kim J. H., Lee Y. C., Cheong J., Lee J. W. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 12470–12474 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

