Receptor interacting protein 3 suppresses vascular smooth muscle cell growth by inhibition of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase-Akt axis
- PMID: 20042608
- PMCID: PMC2843204
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.071332
Receptor interacting protein 3 suppresses vascular smooth muscle cell growth by inhibition of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase-Akt axis
Abstract
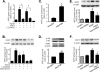
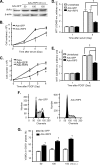
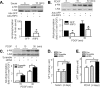
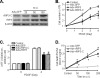
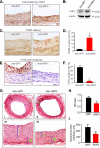
Proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) is a primary mechanism underlying cardiovascular proliferative disorders. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)-Akt (or protein kinase B) axis has been assigned at the center of pathways that regulate cell proliferation. Here we demonstrate that enhanced PI3K-Akt signaling by mitogenic stimulation or arterial injury profoundly elevates expression of receptor interacting protein 3 (RIP3) in primary cultured rat VSMCs and in vivo and that the up-regulation of RIP3 leads to VSMC growth arrest and apoptosis via inhibiting the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, thereby alleviating balloon injury-induced neointimal formation. Specifically, mitogenic stimulation with platelet-derived growth factor-BB or angiotensin II leads to a profound increase in RIP3 expression, which is abolished by inhibition of PI3K or Akt, and increased PI3K-Akt signaling by expression of a constitutively active PI3K mutant also elevates RIP3 expression. Importantly, adenoviral overexpression of RIP3 not only triggers apoptosis but also causes cell cycle arrest at G(1)/G(0) phases that is associated with suppressed Akt activation. In sharp contrast, RIP3 gene silencing enhances serum- and platelet-derived growth factor-induced cell proliferation and Akt activation. In vivo adenoviral gene delivery of rat RIP3 (rRIP3) increased apoptosis and reduced VSMC proliferation, thus, effectively alleviating balloon injury-induced neointimal formation. The growth-suppressive and pro-apoptotic effects are independent of rRIP3 Ser/Thr kinase activity, because overexpression of a kinase-inactive mutant of rRIP3, similar to its wild type, is sufficient to induce growth arrest and apoptosis. These findings reveal a novel growth-suppressive action of RIP3, marking RIP3 as an important factor to prevent excessive mitogenic stimulation- or injury-induced vascular smooth muscle cells hyperplasia.
Figures


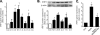
Similar articles
-
Impaired peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma contributes to phenotypic modulation of vascular smooth muscle cells during hypertension.J Biol Chem. 2010 Apr 30;285(18):13666-77. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.087718. Epub 2010 Mar 8. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20212046 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of c-Cbl tyrosine phosphorylation inhibits neointimal formation in balloon-injured rat arteries.Circulation. 2008 Aug 12;118(7):764-72. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.761932. Epub 2008 Jul 28. Circulation. 2008. PMID: 18663086
-
Angiotensin II-induced histone deacetylase 5 phosphorylation, nuclear export, and Egr-1 expression are mediated by Akt pathway in A10 vascular smooth muscle cells.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021 Apr 1;320(4):H1543-H1554. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00683.2020. Epub 2021 Feb 19. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33606583
-
CKLF1 aggravates neointimal hyperplasia by inhibiting apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells through PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Sep;117:108986. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108986. Epub 2019 Jul 10. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31387172
-
TCM Regulates PI3K/Akt Signal Pathway to Intervene Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Dec 16;2021:4854755. doi: 10.1155/2021/4854755. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34956379 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The inhibitory effect of Isoliquiritigenin on the proliferation of human arterial smooth muscle cell.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017 Jul 17;18(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s40360-017-0165-2. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28716056 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor interacting protein kinase 3 (RIP3) regulates iPSCs generation through modulating cell cycle progression genes.Stem Cell Res. 2019 Mar;35:101387. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2019.101387. Epub 2019 Jan 23. Stem Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 30703581 Free PMC article.
-
RIPK3 promotes kidney fibrosis via AKT-dependent ATP citrate lyase.JCI Insight. 2018 Feb 8;3(3):e94979. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.94979. eCollection 2018 Feb 8. JCI Insight. 2018. PMID: 29415885 Free PMC article.
-
Mass Spectrometric Imaging Reveals Temporal and Spatial Dynamics of Bioactive Lipids in Arteries Undergoing Restenosis.J Proteome Res. 2019 Apr 5;18(4):1669-1678. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00941. Epub 2019 Mar 11. J Proteome Res. 2019. PMID: 30784274 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor-interacting protein 1 and 3 kinase activity are required for high-fat diet induced liver injury in mice.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Dec 15;14:1267996. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1267996. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38161978 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Braun-Dullaeus R. C., Mann M. J., Dzau V. J. (1998) Circulation 98, 82–89 - PubMed
-
- Dzau V. J., Braun-Dullaeus R. C., Sedding D. G. (2002) Nat. Med. 8, 1249–1256 - PubMed
-
- Forrester J. S., Fishbein M., Helfant R., Fagin J. (1991) J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 17, 758–769 - PubMed
-
- Novak K. (1998) Nat. Med. 4, 989–990 - PubMed
-
- Ferns G. A., Raines E. W., Sprugel K. H., Motani A. S., Reidy M. A., Ross R. (1991) Science 253, 1129–1132 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

