Molecular mechanism of proinflammatory cytokine-mediated squamous metaplasia in human corneal epithelial cells
- PMID: 20042643
- PMCID: PMC2868474
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.09-4677
Molecular mechanism of proinflammatory cytokine-mediated squamous metaplasia in human corneal epithelial cells
Abstract
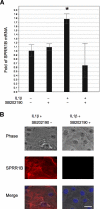
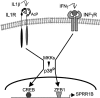
Purpose: The cornified envelope protein small proline-rich protein 1B (SPRR1B) is a biomarker for squamous metaplasia. Proinflammatory cytokines IL-1beta and IFN-gamma are potent inducers of ocular surface keratinization and SPRR1B expression. Here the molecular mechanisms controlling SPRR1B gene expression in response to IL-1beta and IFN-gamma are elucidated.
Methods: A 3-kb fragment of the SPRR1B gene 5'-flanking region was amplified from human chromosome 1, sequentially deleted, and cloned into a luciferase vector. Constructs were transiently transfected into human corneal epithelial cells, and activity was assessed in response to IL-1beta, IFN-gamma, or basal medium. Functional cis-elements responding to IL-1beta and IFN-gamma were characterized by site-directed mutagenesis and gel mobility shift assay. Effects of mitogen-activated protein kinases p38, ERK, and JNK were assessed using inhibitors and dominant-negative mutants. Results were validated by real-time RT-PCR.
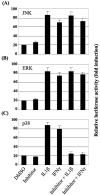
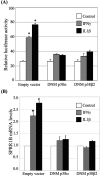
Results: The first 620 bp of the SPRR1B 5'-flanking region regulated constitutive expression and increased promoter activity in response to IL-1beta and IFN-gamma. Corresponding cis-elements for IL-1beta and IFN-gamma were bound by cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) and zinc-finger E-box binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1), respectively. Inhibition of p38 abolished the stimulatory effects of IL-1beta and IFN-gamma on SPRR1B, whereas inhibition of JNK and ERK had no effect. Dominant-negative mutants targeting p38alpha and p38beta2 blocked cytokine-induced SPRR1B promoter activity and mRNA expression.
Conclusions: SPRR1B is upregulated by the proinflammatory cytokines IL-1beta and IFN-gamma via p38 MAPK-mediated signaling pathways that lead to the activation of transcription factors CREB and ZEB1, respectively. These results identify key intracellular signaling intermediates involved in the pathogenesis of immune-mediated ocular surface squamous metaplasia.
Figures


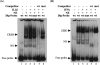

Similar articles
-
Small proline-rich protein 1B (SPRR1B) is a biomarker for squamous metaplasia in dry eye disease.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008 Jan;49(1):34-41. doi: 10.1167/iovs.07-0685. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008. PMID: 18172072 Free PMC article.
-
Defensin expression by the cornea: multiple signalling pathways mediate IL-1beta stimulation of hBD-2 expression by human corneal epithelial cells.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003 May;44(5):1859-65. doi: 10.1167/iovs.02-0787. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003. PMID: 12714616 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of microRNA-146a and microRNA-146b-5p in human retinal pigment epithelial cells by interleukin-1β, tumor necrosis factor-α, and interferon-γ.Mol Vis. 2013 Apr 3;19:737-50. Print 2013. Mol Vis. 2013. PMID: 23592910 Free PMC article.
-
Immune profile of squamous metaplasia development in autoimmune regulator-deficient dry eye.Mol Vis. 2009;15:563-76. Epub 2009 Mar 23. Mol Vis. 2009. PMID: 19365590 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between proximal and distal promoter elements is required for squamous differentiation marker induction in the bronchial epithelium: role for ESE-1, Sp1, and AP-1 proteins.J Biol Chem. 2003 Jun 13;278(24):21378-87. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M212258200. Epub 2003 Apr 7. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12682075
Cited by
-
The Efficacy of 2% Topical Rebamipide on Conjunctival Squamous Metaplasia and Goblet Cell Density in Dry Eye Disease.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Jul/Aug;35(6):350-358. doi: 10.1089/jop.2018.0130. Epub 2019 Jun 28. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 31259647 Free PMC article.
-
Natural killer cells drive 4-1BBL positive uveal melanoma towards EMT and metastatic disease.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Jan 9;43(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02917-5. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38191418 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Exosomes Released by Different Corneal Cell Types on the Wound Healing Properties of Human Corneal Epithelial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 13;23(20):12201. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012201. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293057 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of growth factors on the proliferation and gene expression of human meibomian gland epithelial cells.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013 Apr 5;54(4):2541-50. doi: 10.1167/iovs.12-11221. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013. PMID: 23493293 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of gasdermin D in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and its effect on its biological function.Front Oncol. 2023 Jul 6;13:1163714. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1163714. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37483501 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beitch I. The induction of keratinization in the corneal epithelium: a comparison of the “dry” and vitamin A-deficient eyes. Invest Ophthalmol 1970;9:827–843 - PubMed
-
- Nelson JD, Havener VR, Cameron JD. Cellulose acetate impressions of the ocular surface: dry eye states. Arch Ophthalmol 1983;101:1869–1872 - PubMed
-
- Tseng SC. Staging of conjunctival squamous metaplasia by impression cytology. Ophthalmology 1985;92:728–733 - PubMed
-
- Jones DT, Monroy D, Ji Z, Pflugfelder SC. Alterations of ocular surface gene expression in Sjögren's syndrome. Adv Exp Med Biol 1998;438:533–536 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

