Ectopic T-cell specificity and absence of perforin and granzyme B alleviate neural damage in oligodendrocyte mutant mice
- PMID: 20042681
- PMCID: PMC2808063
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090722
Ectopic T-cell specificity and absence of perforin and granzyme B alleviate neural damage in oligodendrocyte mutant mice
Erratum in
- Am J Pathol. 2010 Oct;177(4):2145
Abstract
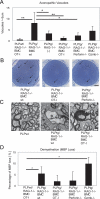
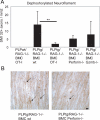
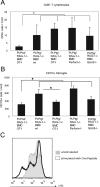
In transgenic mice overexpressing the major myelin protein of the central nervous system, proteolipid protein, CD8+ T-lymphocytes mediate the primarily genetically caused myelin and axon damage. In the present study, we investigated the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying this immune-related neural injury. At first, we investigated whether T-cell receptors (TCRs) are involved in these processes. For this purpose, we transferred bone marrow from mutants carrying TCRs with an ectopic specificity to ovalbumin into myelin mutant mice that also lacked normal intrinsic T-cells. T-lymphocytes with ovalbumin-specific TCRs entered the mutant central nervous system to a similar extent as T-lymphocytes from wild-type mice. However, as revealed by histology, electron microscopy and axon- and myelin-related immunocytochemistry, these T-cells did not cause neural damage in the myelin mutants, reflecting the need for specific antigen recognition by cytotoxic CD8+ T-cells. By chimerization with bone marrow from perforin- or granzyme B (Gzmb)-deficient mice, we demonstrated that absence of these cytotoxic molecules resulted in reduced neural damage in myelin mutant mice. Our study strongly suggests that pathogenetically relevant immune reactions in proteolipid protein-overexpressing mice are TCR-dependent and mediated by the classical components of CD8+ T-cell cytotoxicity, perforin, and Gzmb. These findings have high relevance with regard to our understanding of the pathogenesis of disorders primarily caused by genetically mediated oligodendropathy.
Figures
References
-
- Ip CW, Kroner A, Fischer S, Berghoff M, Kobsar I, Mäurer M, Martini R. Role of immune cells in animal models for inherited peripheral neuropathies. Neuromol Med. 2006;8:175–189. - PubMed
-
- Ip CW, Kroner A, Crocker PR, Nave KA, Martini R. Sialoadhesin deficiency ameliorates myelin degeneration and axonopathic changes in the CNS of PLP overexpressing mice. Neurobiol Dis. 2007;25:105–111. - PubMed
-
- Leder C, Schwab N, Ip CW, Kroner A, Nave KA, Dornmair K, Martini R, Wiendl H. Clonal expansions of pathogenic CD8+ effector cells in the CNS of myelin mutant mice. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2007;36:416–424. - PubMed
-
- Kassmann CM, Lappe-Siefke C, Baes M, Brugger B, Mildner A, Werner HB, Natt O, Michaelis T, Prinz M, Frahm J, Nave KA. Axonal loss and neuroinflammation caused by peroxisome-deficient oligodendrocytes. Nat Genet. 2007;39:969–976. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

