Akt1 and Akt2 promote peripheral B-cell maturation and survival
- PMID: 20042722
- PMCID: PMC2875094
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-09-241638
Akt1 and Akt2 promote peripheral B-cell maturation and survival
Abstract
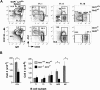
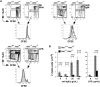
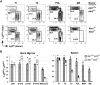
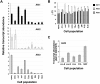
Although the 3 isoforms of Akt regulate cell growth, proliferation, and survival in a wide variety of cell types, their role in B-cell development is unknown. We assessed B-cell maturation in the bone marrow (BM) and periphery in chimeras established with fetal liver progenitors lacking Akt1 and/or Akt2. We found that the generation of marginal zone (MZ) and B1 B cells, 2 key sources of antibacterial antibodies, was highly dependent on the combined expression of Akt1 and Akt2. In contrast, Akt1/2 deficiency did not negatively affect the generation of transitional or mature follicular B cells in the periphery or their precursors in the BM. However, Akt1/2-deficient follicular B cells exhibited a profound survival defect when forced to compete against wild-type B cells in vivo. Altogether, these studies show that Akt signaling plays a key role in peripheral B-cell maturation and survival.
Figures
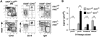
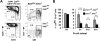
References
-
- Rolink A, Haasner D, Melchers F, Andersson J. The surrogate light chain in mouse B-cell development. Int Rev Immunol. 1996;13(4):341–356. - PubMed
-
- Melchers F, ten Boekel E, Seidl T, et al. Repertoire selection by pre-B-cell receptors and B-cell receptors, and genetic control of B-cell development from immature to mature B cells. Immunol Rev. 2000;175:33–46. - PubMed
-
- Allman DM, Ferguson SE, Lentz VM, Cancro MP. Peripheral B cell maturation: II, heat-stable antigen(hi) splenic B cells are an immature developmental intermediate in the production of long-lived marrow-derived B cells. J Immunol. 1993;151(9):4431–4444. - PubMed
-
- Allman D, Srivastava B, Lindsley RC. Alternative routes to maturity: branch points and pathways for generating follicular and marginal zone B cells. Immunol Rev. 2004;197:147–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

