Human rhinovirus and coronavirus detection among allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients
- PMID: 20042728
- PMCID: PMC2837322
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-09-244152
Human rhinovirus and coronavirus detection among allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients
Abstract
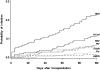
Little is known about clinical and virologic manifestations of rhinovirus (HRV) and coronavirus (HCoV) infections after hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT). We performed surveillance for 1 year and describe the natural history of these infections during the first 100 days after allogeneic HCT, when symptom surveys and upper respiratory samples were collected weekly. Samples were tested using RT-PCR for HRVs and HCoVs (OC43, 229E, HKU1, and NL63). Among 215 patients, 64 (30%) patients had 67 infections. Day 100 cumulative incidence estimate was 22.3% for HRV and 11.1% for HCoV. Median duration of viral shedding was 3 weeks; prolonged shedding of at least 3 months occurred in 6 of 45 patients with HRV and 3 of 22 with HCoV. Six patients with HRV and 9 with HCoV were asymptomatic. HRV infection was associated with rhinorrhea, congestion, postnasal drip, sputum, and cough; HCoV infection was not associated with respiratory symptoms or hepatic dysfunction. Lower respiratory infection developed in 2 patients with HRV before day 100, and 1 each with HRV and HCoV after day 100. HRV and HCoV infections are common in the first 100 days after HCT, viral shedding lasts more than 3 weeks in half, and lower respiratory infection is rare.
Figures

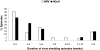
References
-
- Heugel J, Martin ET, Kuypers J, Englund JA. Coronavirus-associated pneumonia in previously healthy children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2007;26(8):753–755. - PubMed
-
- Hicks LA, Shepard CW, Britz PH, et al. Two outbreaks of severe respiratory disease in nursing homes associated with rhinovirus. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54(2):284–289. - PubMed
-
- Nichols WG, Guthrie KA, Corey L, Boeckh M. Influenza infections after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: risk factors, mortality, and the effect of antiviral therapy. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39(9):1300–1306. - PubMed
-
- Nichols WG, Gooley T, Boeckh M. Community-acquired respiratory syncytial virus and parainfluenza virus infections after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center experience. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2001;7(suppl):11S–15S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

