BDNF Val66Met is associated with introversion and interacts with 5-HTTLPR to influence neuroticism
- PMID: 20042999
- PMCID: PMC2840212
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2009.213
BDNF Val66Met is associated with introversion and interacts with 5-HTTLPR to influence neuroticism
Abstract
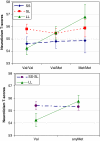
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) regulates synaptic plasticity and neurotransmission, and has been linked to neuroticism, a major risk factor for psychiatric disorders. A recent genome-wide association (GWA) scan, however, found the BDNF Val66Met polymorphism (rs6265) associated with extraversion but not with neuroticism. In this study, we examine the links between BDNF and personality traits, assessed using the Revised NEO Personality Inventory (NEO-PI-R), in a sample from SardiNIA (n=1560) and the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging (BLSA; n=1131). Consistent with GWA results, we found that BDNF Met carriers were more introverted. By contrast, in both samples and in a meta-analysis inclusive of published data (n=15251), we found no evidence for a main effect of BDNF Val66Met on neuroticism. Finally, on the basis of recent reports of an epistatic effect between BDNF and the serotonin transporter, we explored a Val66Met x 5-HTTLPR interaction in a larger SardiNIA sample (n=2333). We found that 5-HTTLPR LL carriers scored lower on neuroticism in the presence of the BDNF Val variant, but scored higher on neuroticism in the presence of the BDNF Met variant. Our findings support the association between the BDNF Met variant and introversion and suggest that BDNF interacts with the serotonin transporter gene to influence neuroticism.
Figures
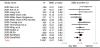
Similar articles
-
Effects of serotonin transporter promoter and BDNF Val66Met genotype on personality traits in a population representative sample of adolescents.Psychiatr Genet. 2011 Oct;21(5):261-4. doi: 10.1097/YPG.0b013e32834371e8. Psychiatr Genet. 2011. PMID: 21206400
-
BDNF Val66met and 5-HTTLPR polymorphisms predict a human in vivo marker for brain serotonin levels.Hum Brain Mapp. 2015 Jan;36(1):313-23. doi: 10.1002/hbm.22630. Epub 2014 Sep 13. Hum Brain Mapp. 2015. PMID: 25220079 Free PMC article.
-
Variants of the serotonin transporter gene and NEO-PI-R Neuroticism: No association in the BLSA and SardiNIA samples.Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2009 Dec 5;150B(8):1070-7. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.30932. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2009. PMID: 19199283 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma BDNF concentration, Val66Met genetic variant and depression-related personality traits.Genes Brain Behav. 2010 Jul;9(5):512-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2010.00579.x. Epub 2010 Mar 22. Genes Brain Behav. 2010. PMID: 20345896 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of BDNF Val66Met polymorphism on cognition in Bipolar Disorder: A review: Special Section on "Translational and Neuroscience Studies in Affective Disorders" Section Editor, Maria Nobile MD, PhD. This Section of JAD focuses on the relevance of translational and neuroscience studies in providing a better understanding of the neural basis of affective disorders. The main aim is to briefly summaries relevant research findings in clinical neuroscience with particular regards to specific innovative topics in mood and anxiety disorders.J Affect Disord. 2019 Jan 15;243:552-558. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2018.07.054. Epub 2018 Jul 24. J Affect Disord. 2019. PMID: 30078664 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic Modulation of Mood Disorders.J Genet Syndr Gene Ther. 2013 Feb 11;4(120):1000120. doi: 10.4172/2157-7412.1000120. J Genet Syndr Gene Ther. 2013. PMID: 23565345 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between BDNF val66met polymorphism and personality on long-term cardiac outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndrome.PLoS One. 2019 Dec 30;14(12):e0226802. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226802. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31887219 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Mind-Body Training on Personality and Behavioral Activation and Inhibition System According to BDNF Val66Met Polymorphism.Psychiatry Investig. 2016 May;13(3):333-40. doi: 10.4306/pi.2016.13.3.333. Epub 2016 May 18. Psychiatry Investig. 2016. PMID: 27247601 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of BDNF Val66Met and 5-HTTLPR polymorphism variants on neural substrates related to sadness and executive function.Genes Brain Behav. 2012 Apr;11(3):352-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2012.00764.x. Epub 2012 Jan 28. Genes Brain Behav. 2012. PMID: 22225729 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral 5-HT2A receptor and serotonin transporter binding in humans are not affected by the val66met BDNF polymorphism status or blood BDNF levels.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2010 Nov;30(11):e1-7. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2010.114. Epub 2010 Aug 25. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2010. PMID: 20736957 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arbelle S, Benjamin J, Golin M, Kremer I, Belmaker RH, Ebstein RP. Relation of shyness in grade school children to the genotype for the long form of the serotonin transporter promoter region polymorphism. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160:671–676. - PubMed
-
- Bienvenu OJ, Samuels JF, Costa PT, Reti IM, Eaton WW, Nestadt G. Anxiety depressive disorders the five-factor model of personality: a higher- lower-order personality trait investigation in a community sample. Depress Anxiety. 2004;20:92–97. - PubMed
-
- Bouchard TJ, Loehlin JC. Genes evolution, personality. Behav Genet. 2001;31:243–273. - PubMed
-
- Bueller JA, Aftab M, Sen S, Gomez-Hassan D, Burmeister M, Zubieta JK. BDNF Val66Met allele is associated with reduced hippocampal volume in healthy subjects. Biol Psychiatry. 2006;59:812–815. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

