Familial risk for mood disorder and the personality risk factor, neuroticism, interact in their association with frontolimbic serotonin 2A receptor binding
- PMID: 20043006
- PMCID: PMC3055406
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2009.218
Familial risk for mood disorder and the personality risk factor, neuroticism, interact in their association with frontolimbic serotonin 2A receptor binding
Abstract
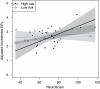
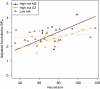
Life stress is a robust risk factor for later development of mood disorders, particularly for individuals at familial risk. Likewise, scoring high on the personality trait neuroticism is associated with an increased risk for mood disorders. Neuroticism partly reflects stress vulnerability and is positively correlated to frontolimbic serotonin 2A (5-HT(2A)) receptor binding. Here, we investigate whether neuroticism interacts with familial risk in relation to frontolimbic 5-HT(2A) receptor binding. Twenty-one healthy twins with a co-twin history of mood disorder and 16 healthy twins without a co-twin history of mood disorder were included. They answered self-report personality questionnaires and underwent [(18)F]altanserin positron emission tomography. We found a significant interaction between neuroticism and familial risk in predicting the frontolimbic 5-HT(2A) receptor binding (p=0.026) in an analysis adjusting for age and body mass index. Within the high-risk group only, neuroticism and frontolimbic 5-HT(2A) receptor binding was positively associated (p=0.0037). In conclusion, our data indicate that familial risk and neuroticism interact in their relation to frontolimbic 5-HT(2A) receptor binding. These findings point at a plausible neurobiological link between genetic and personality risk factors and vulnerability to developing mood disorders. It contributes to our understanding of why some people at high risk develop mood disorders while others do not. We speculate that an increased stress reactivity in individuals at high familial risk for mood disorders might enhance the effect of neuroticism in shaping the impact of potential environmental stress and thereby influence serotonergic neurotransmission.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Frontolimbic serotonin 2A receptor binding in healthy subjects is associated with personality risk factors for affective disorder.Biol Psychiatry. 2008 Mar 15;63(6):569-76. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.07.009. Epub 2007 Sep 19. Biol Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 17884017
-
Gender and the use of hormonal contraception in women are not associated with cerebral cortical 5-HT 2A receptor binding.Neuroscience. 2009 Oct 6;163(2):640-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.06.052. Epub 2009 Jun 25. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19559762
-
Consistent evidence that brain serotonin 2A receptor binding is positively associated with personality-based risk markers of depression.Br J Psychiatry. 2025 Mar;226(3):137-143. doi: 10.1192/bjp.2024.143. Epub 2024 Dec 5. Br J Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 39632615
-
Molecular imaging in patients with mood disorders: a review of PET findings.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011 Jul;38(7):1367-80. doi: 10.1007/s00259-011-1779-z. Epub 2011 Apr 12. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011. PMID: 21484378 Review.
-
Mood, cognition and in vivo protein imaging: the emerging nexus in clinical neuroscience.Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2008 Jun;23(6):555-63. doi: 10.1002/gps.1941. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 18044797 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulating prefrontal cortex activation: an emerging role for the 5-HT₂A serotonin receptor in the modulation of emotion-based actions?Mol Neurobiol. 2013 Dec;48(3):841-53. doi: 10.1007/s12035-013-8472-0. Epub 2013 May 22. Mol Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23696058 Review.
-
Neuroticism predicts the impact of serotonin challenges on fear processing in subgenual anterior cingulate cortex.Sci Rep. 2018 Dec 17;8(1):17889. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36350-y. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30559408 Free PMC article.
-
5-HT radioligands for human brain imaging with PET and SPECT.Med Res Rev. 2013 Jan;33(1):54-111. doi: 10.1002/med.20245. Epub 2011 Jun 14. Med Res Rev. 2013. PMID: 21674551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cerebral 5-HT2A receptor and serotonin transporter binding in humans are not affected by the val66met BDNF polymorphism status or blood BDNF levels.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2010 Nov;30(11):e1-7. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2010.114. Epub 2010 Aug 25. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2010. PMID: 20736957 Free PMC article.
-
Decreases in State and Trait Anxiety Post-psilocybin: A Naturalistic, Observational Study Among Retreat Attendees.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Jul 7;13:883869. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.883869. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35873251 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams KH, Pinborg LH, Svarer C, Hasselbalch SG, Holm S, Haugbol S, et al. A database of [(18)F]-altanserin binding to 5-HT(2A) receptors in normal volunteers: normative data and relationship to physiological and demographic variables. Neuroimage. 2004;21:1105–1113. - PubMed
-
- Akiskal HS, Benazzi F. The DSM-IV and ICD-10 categories of recurrent [major] depressive and bipolar II disorders: evidence that they lie on a dimensional spectrum. J Affect Disord. 2006;92:45–54. - PubMed
-
- Attar-Levy D, Martinot JL, Blin J, Dao-Castellana MH, Crouzel C, Mazoyer B, et al. The cortical serotonin2 receptors studied with positron-emission tomography and [18F]-setoperone during depressive illness and antidepressant treatment with clomipramine. Biol Psychiatry. 1999;45:180–186. - PubMed
-
- Barr CS, Newman TK, Shannon C, Parker C, Dvoskin RL, Becker ML, et al. Rearing condition and rh5-HTTLPR interact to influence limbic-hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis response to stress in infant macaques. Biol Psychiatry. 2004b;55:733–738. - PubMed

