Previous stress attenuates the susceptibility to Midazolam's disruptive effect on fear memory reconsolidation: influence of pre-reactivation D-cycloserine administration
- PMID: 20043007
- PMCID: PMC3055408
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2009.215
Previous stress attenuates the susceptibility to Midazolam's disruptive effect on fear memory reconsolidation: influence of pre-reactivation D-cycloserine administration
Abstract
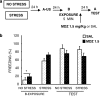
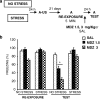
It is well known that, under certain boundary conditions, the retrieval of a stable consolidated memory results into a labile one. During this unstable phase, memory can be vulnerable to interference by a number of pharmacological agents, including benzodiazepines. One of the goals of this study was to evaluate the vulnerability to midazolam (MDZ) after reactivation of recent and remote contextual fear memories in animals that experienced a stressful situation before learning. Animals were subjected to a restraint session and trained in a contextual fear paradigm the following day; consolidated memories were reactivated at different times after learning and different MDZ doses (1.5, 3.0 mg/kg) were administered to rats after reactivation. Our results show that MDZ did not affect memory reconsolidation in older-than-one-day memories of stressed animals, even after the administration of a higher MDZ dose and a longer reactivation session (5 min). In contrast, MDZ was effective in blocking reconsolidation at all memory ages in unstressed animals. In addition, the current research investigated whether activating NMDA sites before reactivation promotes the destabilization of resistant memories such as those of stressed animals. We tested the influence of pre-reactivation D-cycloserine (DCS), a partial NMDA agonist, on MDZ's effect on fear memory reconsolidation in stressed animals. Our findings indicate that DCS before reactivation promotes retrieval-induced lability in resistant memory traces, as MDZ-induced memory impairment in stressed rats became evident with pre-reactivation DCS but not after pre-reactivation sterile isotonic saline.
Figures
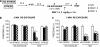
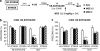
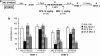
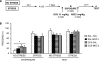
References
-
- Adamec RE, Blundell J, Burton P. Neural circuit changes mediating lasting brain and behavioral response to predator stress. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2005;29:1225–1241. - PubMed
-
- Alberini CM. Mechanisms of memory stabilization: are consolidation and reconsolidation similar or distinct processes. Trends Neurosci. 2005;28:51–56. - PubMed
-
- Anokhin KV, Tiunova AA, Rose SP. Reminder effects: reconsolidation or retrieval deficit? Pharmacological dissection with protein synthesis inhibitors following reminder for a passive-avoidance task in young chicks. Eur J Neurosci. 2002;15:1759–1765. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

