A composite transcriptional signature differentiates responses towards closely related herbicides in Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica napus
- PMID: 20043233
- PMCID: PMC2816244
- DOI: 10.1007/s11103-009-9590-y
A composite transcriptional signature differentiates responses towards closely related herbicides in Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica napus
Abstract
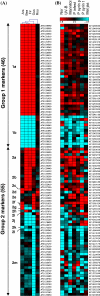
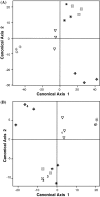
In this study, genome-wide expression profiling based on Affymetrix ATH1 arrays was used to identify discriminating responses of Arabidopsis thaliana to five herbicides, which contain active ingredients targeting two different branches of amino acid biosynthesis. One herbicide contained glyphosate, which targets 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS), while the other four herbicides contain different acetolactate synthase (ALS) inhibiting compounds. In contrast to the herbicide containing glyphosate, which affected only a few transcripts, many effects of the ALS inhibiting herbicides were revealed based on transcriptional changes related to ribosome biogenesis and translation, secondary metabolism, cell wall modification and growth. The expression pattern of a set of 101 genes provided a specific, composite signature that was distinct from other major stress responses and differentiated among herbicides targeting the same enzyme (ALS) or containing the same chemical class of active ingredient (sulfonylurea). A set of homologous genes could be identified in Brassica napus that exhibited a similar expression pattern and correctly distinguished exposure to the five herbicides. Our results show the ability of a limited number of genes to classify and differentiate responses to closely related herbicides in A. thaliana and B. napus and the transferability of a complex transcriptional signature across species.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inheritance and Molecular Characterization of a Novel Mutated AHAS Gene Responsible for the Resistance of AHAS-Inhibiting Herbicides in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.).Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 17;21(4):1345. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041345. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32079260 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct non-target site mechanisms endow resistance to glyphosate, ACCase and ALS-inhibiting herbicides in multiple herbicide-resistant Lolium rigidum.Planta. 2009 Sep;230(4):713-23. doi: 10.1007/s00425-009-0981-8. Epub 2009 Jul 15. Planta. 2009. PMID: 19603180
-
In-silico analysis and expression profiling implicate diverse role of EPSPS family genes in regulating developmental and metabolic processes.BMC Res Notes. 2014 Jan 22;7:58. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-7-58. BMC Res Notes. 2014. PMID: 24450620 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance to AHAS inhibitor herbicides: current understanding.Pest Manag Sci. 2014 Sep;70(9):1340-50. doi: 10.1002/ps.3710. Epub 2014 Jan 20. Pest Manag Sci. 2014. PMID: 24338926 Review.
-
Overview of herbicide mechanisms of action.Environ Health Perspect. 1990 Jul;87:263-71. doi: 10.1289/ehp.9087263. Environ Health Perspect. 1990. PMID: 1980104 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ALOMYbase, a resource to investigate non-target-site-based resistance to herbicides inhibiting acetolactate-synthase (ALS) in the major grass weed Alopecurus myosuroides (black-grass).BMC Genomics. 2015 Aug 12;16(1):590. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1804-x. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26265378 Free PMC article.
-
Cytological and comparative proteomic analyses on male sterility in Brassica napus L. induced by the chemical hybridization agent monosulphuron ester sodium.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 14;8(11):e80191. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080191. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24244648 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Transcriptional Profiling and Metabolic Analysis Uncover Multiple Molecular Responses of the Grass Species Lolium perenne Under Low-Intensity Xenobiotic Stress.Front Plant Sci. 2015 Dec 17;6:1124. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.01124. eCollection 2015. Front Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 26734031 Free PMC article.
-
Physiology and toxicology of hormone-disrupting chemicals in higher plants.Plant Cell Rep. 2013 Jun;32(6):933-41. doi: 10.1007/s00299-013-1428-z. Epub 2013 Apr 4. Plant Cell Rep. 2013. PMID: 23553555 Review.
-
Protein kinase GCN2 mediates responses to glyphosate in Arabidopsis.BMC Plant Biol. 2015 Jan 21;15:14. doi: 10.1186/s12870-014-0378-0. BMC Plant Biol. 2015. PMID: 25603772 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson WP. Weed science: principles. 3. St. Paul: West Publishing Co.; 1996. p. 388.
-
- Aubert S, Bligny R, Day DA, Whelan J, Douce R. Induction of alternative oxidase synthesis by herbicides inhibiting branched chain amino acid synthesis. Plant J. 1997;11:649–657. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1997.11040649.x. - DOI
-
- Brazier-Hicks M, Offen WA, Gershater MC, Revett TJ, Lim EK, Bowles DJ, Davies GJ, Edwards R. Characterization and engineering of the bifunctional N- and O-glucosyltransferase involved in xenobiotic metabolism in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:20238–20243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0706421104. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

