Changes in the expression of methionine adenosyltransferase genes and S-adenosylmethionine homeostasis during hepatic stellate cell activation
- PMID: 20043323
- PMCID: PMC2905860
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.23411
Changes in the expression of methionine adenosyltransferase genes and S-adenosylmethionine homeostasis during hepatic stellate cell activation
Abstract
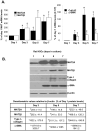
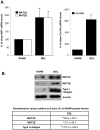
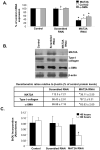
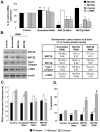
Hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation is an essential event during liver fibrogenesis. Methionine adenosyltransferase (MAT) catalyzes biosynthesis of S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe), the principle methyl donor. SAMe metabolism generates two methylation inhibitors, methylthioadenosine (MTA) and S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH). Liver cell proliferation is associated with induction of two nonliver-specific MATs: MAT2A, which encodes the catalytic subunit alpha2, and MAT2beta, which encodes a regulatory subunit beta that modulates the activity of the MAT2A-encoded isoenzyme MATII. We reported that MAT2A and MAT2beta genes are required for liver cancer cell growth that is induced by the profibrogenic factor leptin. Also, MAT2beta regulates leptin signaling. The strong association of MAT genes with proliferation and leptin signaling in liver cells led us to examine the role of these genes during HSC activation. MAT2A and MAT2beta are induced in culture-activated primary rat HSCs and HSCs from 10-day bile duct ligated (BDL) rat livers. HSC activation led to a decline in intracellular SAMe and MTA levels, a drop in the SAMe/SAH ratio, and global DNA hypomethylation. The decrease in SAMe levels was associated with lower MATII activity during activation. MAT2A silencing in primary HSCs and MAT2A or MAT2beta silencing in the human stellate cell line LX-2 resulted in decreased collagen and alpha-smooth muscle actin (alpha-SMA) expression and cell growth and increased apoptosis. MAT2A knockdown decreased intracellular SAMe levels in LX-2 cells. Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase signaling in LX-2 cells required the expression of MAT2beta but not that of MAT2A.
Conclusion: MAT2A and MAT2beta genes are induced during HSC activation and are essential for this process. The SAMe level falls, resulting in global DNA hypomethylation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Leptin's mitogenic effect in human liver cancer cells requires induction of both methionine adenosyltransferase 2A and 2beta.Hepatology. 2008 Feb;47(2):521-31. doi: 10.1002/hep.22064. Hepatology. 2008. PMID: 18041713 Free PMC article.
-
Pleiotropic effects of methionine adenosyltransferases deregulation as determinants of liver cancer progression and prognosis.J Hepatol. 2013 Oct;59(4):830-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.04.031. Epub 2013 May 7. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23665184 Review.
-
Transcriptional regulation of methionine adenosyltransferase 2A by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in rat hepatic stellate cells.Hepatology. 2012 Jun;55(6):1942-53. doi: 10.1002/hep.25594. Epub 2012 Apr 23. Hepatology. 2012. PMID: 22271545 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin promotes methionine adenosyltransferase 2A expression in hepatic stellate cells by the downregulation of E2F-4 via the β-catenin pathway.FASEB J. 2020 Apr;34(4):5578-5589. doi: 10.1096/fj.201903021RR. Epub 2020 Feb 28. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 32108965
-
Role of methionine adenosyltransferase and S-adenosylmethionine in alcohol-associated liver cancer.Alcohol. 2005 Apr;35(3):227-34. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2005.03.011. Alcohol. 2005. PMID: 16054984 Review.
Cited by
-
Acetylation of MAT IIα represses tumour cell growth and is decreased in human hepatocellular cancer.Nat Commun. 2015 Apr 30;6:6973. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7973. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 25925782 Free PMC article.
-
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms of ALDH18A1 and MAT2A Genes and Their Genetic Associations with Milk Production Traits of Chinese Holstein Cows.Genes (Basel). 2022 Aug 12;13(8):1437. doi: 10.3390/genes13081437. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36011348 Free PMC article.
-
S-adenosylmethionine in liver health, injury, and cancer.Physiol Rev. 2012 Oct;92(4):1515-42. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00047.2011. Physiol Rev. 2012. PMID: 23073625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MAT2B mediates invasion and metastasis by regulating EGFR signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.Clin Exp Med. 2019 Nov;19(4):535-546. doi: 10.1007/s10238-019-00579-2. Epub 2019 Sep 6. Clin Exp Med. 2019. PMID: 31493275
-
Role of methionine adenosyltransferase α2 and β phosphorylation and stabilization in human hepatic stellate cell trans-differentiation.J Cell Physiol. 2015 May;230(5):1075-85. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24839. J Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25294683 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burt AD. Cellular and molecular aspects of hepatic fibrosis. J Pathol. 1993;70:105–114. - PubMed
-
- Gressner AM, Weiskirchen R, Breitkopf K, Dooley S. Roles of TGF-beta in hepatic fibrosis. Front Biosci. 2002;7:d793–807. - PubMed
-
- Paradis V, Dargere D, Bonvoust F, Vidaud M, Segarini P, Bedossa P. Effects and regulation of connective tissue growth factor on hepatic stellate cells. Lab Invest. 2002;82:767–774. - PubMed
-
- Kamphorst BE, Stoll D, Gressner AM, Weiskirchen R. Inhibitory effect of soluble PDGF-beta receptor in culture-activated hepatic stellate cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;317:451–462. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
