Fractionated evaluation of immunohistochemical hormone receptor expression enhances prognostic prediction in breast cancer patients treated with tamoxifen as adjuvant therapy
- PMID: 20043345
- PMCID: PMC2801083
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B0900295
Fractionated evaluation of immunohistochemical hormone receptor expression enhances prognostic prediction in breast cancer patients treated with tamoxifen as adjuvant therapy
Abstract
Objective: To compare the prognostic prediction between dichotomized and fractionated evaluations of hormone receptor expressions.
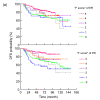
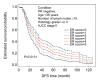
Methods: Patients with stages I-III breast cancers, who received adjuvant tamoxifen, were enrolled. The expression of estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR) was evaluated by immunohistochemistry (IHC). A fractionated score (F score), the percentage of positive-staining nuclei (0=none, 1=1%-10%, 2=11%-30%, 3=31%-50%, 4=51%-70%, and 5=71%-100%), was assigned to each case. The dichotomized scoring method defines an F score >1 as positive. The prognostic values of both scores were compared by multiple Cox's proportional hazard models of disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS).
Results: Four hundred and sixteen patients with a median follow-up of 78.0 months were included. F scores for ER and PR correlated directly with DFS and OS. Although both the dichotomized and fractionated ER and PR scores were significantly associated with DFS and OS in univariate analyses, only fractionated ER and PR scores remained as independent prognostic factors of DFS and OS in the final multiple Cox's proportional hazard models.
Conclusion: Fractionated IHC hormone receptor expression evaluation enhances the prognostic prediction compared with a dichotomized assessment.
Figures







References
-
- Arpino G, Weiss H, Lee AV, Schiff R, de Placido S, Osborne CK, Elledge RM. Estrogen receptor-positive, progesterone receptor-negative breast cancer: association with growth factor receptor expression and tamoxifen resistance. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97(17):1254–1261. - PubMed
-
- Badve SS, Baehner FL, Gray RP, Childs BH, Maddala T, Liu ML, Rowley SC, Shak S, Perez EA, Shulman LJ, et al. Estrogen- and progesterone-receptor status in ECOG 2197: comparison of immunohistochemistry by local and central laboratories and quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction by central laboratory. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(15):2473–2481. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.13.6424. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

