Identification of four novel phosphorylation sites in estrogen receptor alpha: impact on receptor-dependent gene expression and phosphorylation by protein kinase CK2
- PMID: 20043841
- PMCID: PMC2811108
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2091-10-36
Identification of four novel phosphorylation sites in estrogen receptor alpha: impact on receptor-dependent gene expression and phosphorylation by protein kinase CK2
Abstract
Background: Estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) phosphorylation is important for estrogen-dependent transcription of ER-dependent genes, ligand-independent receptor activation and endocrine therapy response in breast cancer. However ERalpha phosphorylation at the previously identified sites does not fully account for these receptor functions. To determine if additional ERalpha phosphorylation sites exist, COS-1 cells expressing human ERalpha were labeled with [32P]H3PO4 in vivo and ERalpha tryptic phosphopeptides were isolated to identify phosphorylation sites.
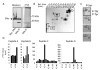
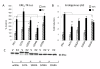
Results: Previously uncharacterized phosphorylation sites at serines 46/47, 282, 294, and 559 were identified by manual Edman degradation and phosphoamino acid analysis and confirmed by mutagenesis and phospho-specific antibodies. Antibodies detected phosphorylation of endogenous ERalpha in MCF-7, MCF-7-LCC2, and Ishikawa cancer cell lines by immunoblot. Mutation of Ser-282 and Ser-559 to alanine (S282A, S559A) resulted in ligand independent activation of ERalpha as determined by both ERE-driven reporter gene assays and endogenous pS2 gene expression in transiently transfected HeLa cells. Mutation of Ser-46/47 or Ser-294 to alanine markedly reduced estradiol dependent reporter activation. Additionally protein kinase CK2 was identified as a kinase that phosphorylated ERalpha at S282 and S559 using motif analysis, in vitro kinase assays, and incubation of cells with CK2 kinase inhibitor.
Conclusion: These novel ERalpha phosphorylation sites represent new means for modulation of ERalpha activity. S559 represents the first phosphorylation site identified in the extreme C-terminus (F domain) of a steroid receptor.
Figures
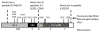


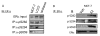

Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation at serines 104 and 106 by Erk1/2 MAPK is important for estrogen receptor-alpha activity.J Mol Endocrinol. 2008 Apr;40(4):173-84. doi: 10.1677/JME-07-0165. J Mol Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18372406 Free PMC article.
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 interacts with and phosphorylates estrogen receptor alpha and is involved in the regulation of receptor activity.J Biol Chem. 2005 Sep 23;280(38):33006-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M506758200. Epub 2005 Aug 1. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16076840
-
Protein kinase A exhibits selective modulation of estradiol-dependent transcription in breast cancer cells that is associated with decreased ligand binding, altered estrogen receptor alpha promoter interaction, and changes in receptor phosphorylation.Mol Endocrinol. 2007 Feb;21(2):439-56. doi: 10.1210/me.2006-0059. Epub 2006 Oct 26. Mol Endocrinol. 2007. PMID: 17068199
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 protects estrogen receptor alpha from proteasomal degradation and is required for full transcriptional activity of the receptor.Mol Endocrinol. 2007 Oct;21(10):2427-39. doi: 10.1210/me.2007-0129. Epub 2007 Jul 3. Mol Endocrinol. 2007. PMID: 17609434
-
Estrogen receptor alpha phosphorylation and its functional impact in human breast cancer.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015 Dec 15;418 Pt 3:264-72. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2015.01.016. Epub 2015 Jan 15. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25597633 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphorylation of S122 in ERα is important for the skeletal response to estrogen treatment in male mice.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 27;12(1):22449. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-26939-9. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36575297 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Kinase CK2 Expression Predicts Relapse Survival in ERα Dependent Breast Cancer, and Modulates ERα Expression in Vitro.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015 Dec 22;13(1):ijerph13010036. doi: 10.3390/ijerph13010036. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015. PMID: 26703694 Free PMC article.
-
Stable inhibition of specific estrogen receptor α (ERα) phosphorylation confers increased growth, migration/invasion, and disruption of estradiol signaling in MCF-7 breast cancer cells.Endocrinology. 2012 Sep;153(9):4144-59. doi: 10.1210/en.2011-2001. Epub 2012 Jun 25. Endocrinology. 2012. PMID: 22733972 Free PMC article.
-
Endocrine Resistance in Breast Cancer: The Role of Estrogen Receptor Stability.Cells. 2020 Sep 11;9(9):2077. doi: 10.3390/cells9092077. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32932819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylation of Farnesoid X Receptor at Serine 154 Links Ligand Activation With Degradation.Mol Endocrinol. 2016 Oct;30(10):1070-1080. doi: 10.1210/me.2016-1105. Epub 2016 Aug 29. Mol Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 27571290 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dutertre M, Smith CL. Ligand-Independent Interactions of p160/Steroid Receptor Coactivators and CREB-Binding Protein (CBP) with Estrogen Receptor-{alpha}: Regulation by Phosphorylation Sites in the A/B Region Depends on Other Receptor Domains. Mol Endocrinol. 2003;17:1296–1314. doi: 10.1210/me.2001-0316. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shah YM, Rowan BG. The Src kinase pathway promotes tamoxifen agonist action in Ishikawa endometrial cells through phosphorylation-dependent stabilization of estrogen receptor (alpha) promoter interaction and elevated steroid receptor coactivator 1 activity. Mol Endocrinol. 2005;19:732–748. doi: 10.1210/me.2004-0298. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

