Negative charge of the glutamic acid 417 residue is crucial for isomerohydrolase activity of RPE65
- PMID: 20043869
- PMCID: PMC2812700
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.12.149
Negative charge of the glutamic acid 417 residue is crucial for isomerohydrolase activity of RPE65
Abstract
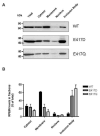
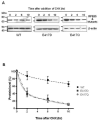
RPE65 is the isomerohydrolase essential for regeneration of 11-cis retinal, the chromophore of visual pigments. Here we compared the impacts of two mutations in RPE65, E417Q identified in patients with Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA), and E417D on isomerohydrolase activity. Although both mutations decreased the stability of RPE65 and altered its sub-cellular localization, E417Q abolished isomerohydrolase activity whereas the E417D mutant retained partial enzymatic activity suggesting that the negative charge of E417 is important for RPE65 catalytic activity. Loss of charge at this position may represent a mechanism by which the E417Q mutation causes blindness in LCA patients.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Membrane-binding and enzymatic properties of RPE65.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2010 Sep;29(5):428-42. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2010.03.002. Epub 2010 Mar 19. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2010. PMID: 20304090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impacts of two point mutations of RPE65 from Leber's congenital amaurosis on the stability, subcellular localization and isomerohydrolase activity of RPE65.FEBS Lett. 2006 Jul 24;580(17):4200-4. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.06.078. Epub 2006 Jul 5. FEBS Lett. 2006. PMID: 16828753
-
RPE65 from cone-dominant chicken is a more efficient isomerohydrolase compared with that from rod-dominant species.J Biol Chem. 2008 Mar 28;283(13):8110-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M703654200. Epub 2008 Jan 23. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18216020 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation of key residues of RPE65 abolishes its enzymatic role as isomerohydrolase in the visual cycle.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Sep 20;102(38):13658-63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504167102. Epub 2005 Sep 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16150724 Free PMC article.
-
Leber congenital amaurosis due to RPE65 mutations and its treatment with gene therapy.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2010 Sep;29(5):398-427. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2010.04.002. Epub 2010 Apr 24. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2010. PMID: 20399883 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Membrane-binding and enzymatic properties of RPE65.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2010 Sep;29(5):428-42. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2010.03.002. Epub 2010 Mar 19. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2010. PMID: 20304090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Key Residues for Catalytic Function and Metal Coordination in a Carotenoid Cleavage Dioxygenase.J Biol Chem. 2016 Sep 9;291(37):19401-12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.744912. Epub 2016 Jul 24. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27453555 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Amelioration of Cone Survival and Vision in a Mouse Model for Leber Congenital Amaurosis.J Neurosci. 2016 May 25;36(21):5808-19. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3857-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27225770 Free PMC article.
-
Higher throughput assays for understanding the pathogenicity of variants of unknown significance (VUS) in the RPE65 gene.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 5:2025.01.31.635952. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.31.635952. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39975398 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Retinal pigment epithelium 65 kDa protein (RPE65): An update.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2022 May;88:101013. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2021.101013. Epub 2021 Oct 2. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2022. PMID: 34607013 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hamel CP, Tsilou E, Harris E, Pfeffer BA, Hooks JJ, Detrick B, Redmond TM. A developmentally regulated microsomal protein specific for the pigment epithelium of the vertebrate retina. J Neurosci Res. 1993;34:414–425. - PubMed
-
- Strauss O. The Retinal Pigment Epithelium in Visual Function. Physiol Rev. 2005;85:845–881. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

