Muscle cells enhance resistance to pro-inflammatory cytokine-induced cartilage destruction
- PMID: 20043873
- PMCID: PMC2841304
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.12.138
Muscle cells enhance resistance to pro-inflammatory cytokine-induced cartilage destruction
Abstract
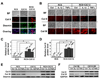
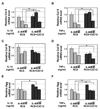
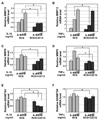
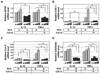
Pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1beta and TNFalpha play important roles in the manifestation of arthritis by disrupting the anabolic and catabolic activities of the chondrocytes. We observed a novel mechanism of cartilage regulation by which muscle cells diminish the response of chondrocytes to IL-1beta and TNFalpha. We found that chondrocytes cocultured with muscle cells or cultured in muscle cell-conditioned medium significantly enhanced the expression of cartilage matrix proteins (collagen II and collagen IX) and resisted IL-1beta and TNFalpha-induced cartilage damage. Our data suggest that this effect is achieved by inhibiting the expression of key components of the signaling pathways of pro-inflammatory cytokines (including NFkappaB, ESE-1, Cox-2, and GADD45beta), leading to attenuated expression of cartilage-degrading enzymes (MMPs and ADAMTS4). Therefore, our work unveils a potential role of muscle in regulating cartilage homeostasis and response to pro-inflammatory stimuli, and provides insights on designing treatment strategies for joint degenerative diseases such as arthritis.
Copyright (c) 2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Blaschke UK, Eikenberry EF, Hulmes DJ, et al. Collagen XI nucleates self-assembly and limits lateral growth of cartilage fibrils. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:10370–10378. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

