RepD-mediated recruitment of PcrA helicase at the Staphylococcus aureus pC221 plasmid replication origin, oriD
- PMID: 20044350
- PMCID: PMC2847222
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp1153
RepD-mediated recruitment of PcrA helicase at the Staphylococcus aureus pC221 plasmid replication origin, oriD
Abstract
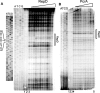
Plasmid encoded replication initiation (Rep) proteins recruit host helicases to plasmid replication origins. Previously, we showed that RepD recruits directionally the PcrA helicase to the pC221 oriD, remains associated with it, and increases its processivity during plasmid unwinding. Here we show that RepD forms a complex extending upstream and downstream of the core oriD. Binding of RepD causes remodelling of a region upstream from the core oriD forming a 'landing pad' for the PcrA. PcrA is recruited by this extended RepD-DNA complex via an interaction with RepD at this upstream site. PcrA appears to have weak affinity for this region even in the absence of RepD. Upon binding of ADPNP (non-hydrolysable analogue of ATP), by PcrA, a conformational rearrangement of the RepD-PcrA-ATP initiation complex confines it strictly within the boundaries of the core oriD. We conclude that RepD-mediated recruitment of PcrA at oriD is a three step process. First, an extended RepD-oriD complex includes a region upstream from the core oriD; second, the PcrA is recruited to this upstream region and thirdly upon ATP-binding PcrA relocates within the core oriD.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Directional loading and stimulation of PcrA helicase by the replication initiator protein RepD.J Mol Biol. 2007 Aug 10;371(2):336-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.05.050. Epub 2007 May 24. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17574572
-
In vitro studies of the initiation of staphylococcal plasmid replication. Specificity of RepD for its origin (oriD) and characterization of the Rep-ori tyrosyl ester intermediate.J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5519-30. J Biol Chem. 1990. PMID: 2156820
-
Plasmid replication initiator protein RepD increases the processivity of PcrA DNA helicase.Nucleic Acids Res. 1999 Mar 15;27(6):1421-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/27.6.1421. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999. PMID: 10037801 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies for helicase recruitment and loading in bacteria.EMBO Rep. 2003 Jan;4(1):37-41. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.embor703. EMBO Rep. 2003. PMID: 12524518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial replication initiator DnaA. Rules for DnaA binding and roles of DnaA in origin unwinding and helicase loading.Biochimie. 2001 Jan;83(1):5-12. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(00)01216-5. Biochimie. 2001. PMID: 11254968 Review.
Cited by
-
A conserved helicase processivity factor is needed for conjugation and replication of an integrative and conjugative element.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(1):e1003198. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003198. Epub 2013 Jan 10. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23326247 Free PMC article.
-
The SF1 helicase encoded by the archaeal plasmid pTN2 of Thermococcus nautili.Extremophiles. 2014 Jul;18(4):779-87. doi: 10.1007/s00792-014-0658-5. Epub 2014 Jun 3. Extremophiles. 2014. PMID: 24889120
-
Analysis of the PcrA-RNA polymerase complex reveals a helicase interaction motif and a role for PcrA/UvrD helicase in the suppression of R-loops.Elife. 2021 Jul 19;10:e68829. doi: 10.7554/eLife.68829. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34279225 Free PMC article.
-
Protein structure. Engineering of a superhelicase through conformational control.Science. 2015 Apr 17;348(6232):344-7. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa0445. Science. 2015. PMID: 25883358 Free PMC article.
-
Bringing them together: plasmid pMV158 rolling circle replication and conjugation under an evolutionary perspective.Plasmid. 2014 Jul;74:15-31. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2014.05.004. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Plasmid. 2014. PMID: 24942190 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gillespie MT, Skurray RA. Structural relationships among chloramphenicol-resistance plasmids of Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1988;51:205–210.
-
- Daini OA, Akano SA. Plasmid-mediated antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus from patients and non-patients. Sci. Res. Essay. 2009;4:346–350.
-
- Khan SA. Plasmid rolling-circle replication: recent developments. Mol. Microbiol. 2000;37:477–484. - PubMed
-
- Novick RP. Staphylococcal plasmids and their replication. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 1989;43:537–565. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/E006450/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBF0111561/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/D526502/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/E004717/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

