Lung tumor growth is stimulated in IFN-gamma-/- mice and inhibited in IL-4Ralpha-/- mice
- PMID: 20044622
- PMCID: PMC2860728
Lung tumor growth is stimulated in IFN-gamma-/- mice and inhibited in IL-4Ralpha-/- mice
Abstract
Background: Alternative (M2) macrophage activation is associated with tumor development in many tumor types, including those in the lung. Herein the biological consequences of forcing classical (M1) or alternative (M2) macrophage activation on lung tumor development are examined.
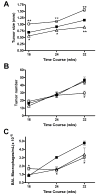
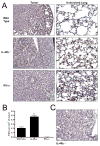
Materials and methods: Urethane-induced lung tumor multiplicity and size were compared in IFN-gamma(-/-) mice which lack M1 macrophage activation, IL-4Ralpha(-/-) mice which lack M2 macrophage activation, and wild-type BALB/cJ (background strain of the IFN-gamma(-/-) and IL-4Ralpha(-/-) mice) mice. Tumor-associated macrophage (TAM) and bone marrow-derived monocyte (BDMC) activation were each examined.
Results: The TAMs and BDMCs in the IFN-gamma(-/-) mice exhibited M2 activation, and their lung tumors were significantly larger than those in the wild-type mice. In contrast, urethane-treated IL-4Ralpha(-/-) mice, whose TAMs and BDMCs were M1 activated, developed smaller tumors than the wild-type mice.
Conclusion: Altered innate immunity can diminish or accelerate lung tumor progression in response to defective cytokine signaling.
Figures

References
-
- Johnson SK, Kerr KM, Chapman AD, Kennedy MM, King G, Cockburn JS, Jeffrey RR. Immune cell infiltrates and prognosis in primary carcinoma of the lung. Lung Cancer. 2000;27:27–35. - PubMed
-
- Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A, Kakolyris S, O'Byrne KJ, Apostolikas N, Skarlatos J, Gatter KC, Harris AL. Different patterns of stromal and cancer cell thymidine phosphorylase reactivity in non-small-cell lung cancer: impact on tumour neoangiogenesis and survival. Br J Cancer. 1998;77:1696–1703. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Takanami I, Takeuchi K, Kodaira S. Tumor-associated macrophage infiltration in pulmonary adenocarcinoma: association with angiogenesis and poor prognosis. Oncology. 1999;57:138–142. - PubMed
-
- Bauer AK, Dwyer-Nield LD, Keil K, Koski K, Malkinson AM. Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) induction of pulmonary inflammation: a role in tumor promotion. Exp Lung Res. 2001;27:197–216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
