Decreased NKCC1 activity in erythrocytes from African Americans with hypertension and dyslipidemia
- PMID: 20044742
- PMCID: PMC3727424
- DOI: 10.1038/ajh.2009.249
Decreased NKCC1 activity in erythrocytes from African Americans with hypertension and dyslipidemia
Abstract
Background: Recent studies demonstrated a key role of ubiquitous isoform of Na+,K+,2Cl- co-transport (NKCC1) in regulation of myogenic tone and peripheral resistance. We examined the impact of race, gender, and plasma lipid on NKCC1 activity in French Canadians and African Americans with hypertension and dyslipidemia.
Methods: NKCC and passive erythrocyte membrane permeability to K+, measured as ouabain-resistant, bumetanide-sensitive, and (ouabain+bumetanide)-resistant 86Rb influx, respectively, were compared in 111 French-Canadian men, 107 French-Canadian women, 26 African-American men, and 45 African-American women with essential hypertension and dyslipidemia.
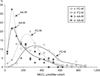
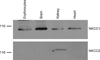
Results: The African-American men and women were 7 years younger and presented twofold decreased plasma triglycerides compared to their French-Canadian counterparts (P < 0.01) whereas body mass index (BMI), total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein, and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) were not different. NKCC was respectively 50 and 38% lower in the African-American men and women than in the French Canadians (P < 0.005) without any differences in passive erythrocyte membrane permeability for K+. We did not observe any impact of age on NKCC in all groups under investigation, whereas plasma triglycerides correlated positively with the activity of this carrier in the French-Canadian men only.
Conclusions: NKCC1 activity is lower in erythrocytes of African Americans with essential hypertension and dyslipidemia than in Caucasian counterparts. We suggest that decreased NKCC1 may contribute to the feature of the pathogenesis of salt-sensitive hypertension seen in African Americans.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sibling resemblance of erythrocyte ion transporters in French-Canadian sibling-pairs affected with essential hypertension.J Hypertens. 1999 Dec;17(12 Pt 2):1859-65. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199917121-00013. J Hypertens. 1999. PMID: 10703881
-
Effect of the Na-K-2Cl cotransporter NKCC1 on systemic blood pressure and smooth muscle tone.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007 May;292(5):H2100-5. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01402.2006. Epub 2007 Jan 26. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17259435 Free PMC article.
-
Relationships between membrane lipids and ion transport in red blood cells of Dahl rats.Life Sci. 2005 Aug 12;77(13):1452-64. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2005.03.014. Life Sci. 2005. PMID: 15936778
-
The role of Na-K-Cl co-transporter in cerebral ischemia.Neurol Res. 2005 Apr;27(3):280-6. doi: 10.1179/016164105X25243. Neurol Res. 2005. PMID: 15845211 Review.
-
NKCC1 and hypertension: role in the regulation of vascular smooth muscle contractions and myogenic tone.Ann Med. 2012 Jun;44 Suppl 1:S111-8. doi: 10.3109/07853890.2011.653395. Ann Med. 2012. PMID: 22713139 Review.
Cited by
-
NKCC1 and NKCC2: The pathogenetic role of cation-chloride cotransporters in hypertension.Genes Dis. 2015 Jun;2(2):186-196. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2015.02.007. Genes Dis. 2015. PMID: 26114157 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish WNK lysine deficient protein kinase 1 (wnk1) affects angiogenesis associated with VEGF signaling.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 29;9(8):e106129. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106129. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25171174 Free PMC article.
-
Volume regulation in mammalian skeletal muscle: the role of sodium-potassium-chloride cotransporters during exposure to hypertonic solutions.J Physiol. 2011 Jun 1;589(Pt 11):2887-99. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.206730. Epub 2011 Apr 11. J Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21486779 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study of red blood cell traits in Hispanics/Latinos: The Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos.PLoS Genet. 2017 Apr 28;13(4):e1006760. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006760. eCollection 2017 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 28453575 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Postnov YU, Orlov S, Gulak P, Shevchenko A. Altered permeability of the erythrocyte membrane for sodium and potassium ions in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Pflugers Arch. 1976;365:257–263. - PubMed
-
- Friedman SM, Nakashima M, McIndoe RA, Friedman CL. Increased erythrocyte permeability to Li and Na in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Experientia. 1976;32:476–478. - PubMed
-
- Orlov SN, Adragna NC, Adarichev VA, Hamet P. Genetic and biochemical determinants of abnormal monovalent ion transport in primary hypertension. Am J Physiol. 1999;276:C511–C536. - PubMed
-
- Orlov SN. Hypertension. In: Bernhardt I, Ellory JC, editors. Red Cell Membrane Transport in Health and Disease. Springer: Berlin; 2003. pp. 587–602.
-
- Garay RP, Alda O. What can we learn from erythrocyte Na-K-Cl cotransporter NKCC1 in human hypertension. Pathophysiology. 2007;14:167–170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

