Effects of epsilon4 on object recognition in the non-demented elderly
- PMID: 20044903
- PMCID: PMC4849126
- DOI: 10.2174/1874609811003020127
Effects of epsilon4 on object recognition in the non-demented elderly
Abstract
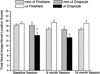
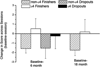
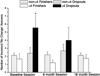
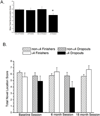
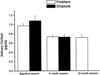
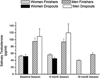
Previously we reported that apolipoprotein E (ApoE) epsilon4 negatively affects performance in the novel-image-novel-location (NINL) object recognition test in healthy non-demented elderly human study participants. In this study, the participants were invited to return for testing sessions 6 and 18 months after the baseline session. Using a longitudinal study design, effects of epsilon4 on NINL test performance were assessed in study "dropouts", participants that did not return for the second and/or third session(s), and "finishers", participants that returned for all sessions. There were effects of epsilon4 on dropout rates and NINL total scores as well as sub-scores in both dropouts and finishers. NINL total score was a predictor of epsilon4 participant dropout. Compared to non-epsilon4 dropouts, epsilon4 dropouts had lower NINL scores. In contrast, epsilon4 finishers had higher NINL scores than non-epsilon4 finishers. Thus, the NINL test could be a valuable tool in detecting pre-clinical signs of age-related cognitive impairments, particularly those associated with epsilon4 risk.
Figures
References
-
- Mahley RW. Apolipoprotein E: Cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science. 1988;240:622–630. - PubMed
-
- De Blasi S, et al. APOE polymorphism affects episodic memory among non demented elderly subjects. Exp Gerontol. 2008 - PubMed
-
- Reynolds CA, et al. Longitudinal memory performance during normal aging: twin association models of APOE and other Alzheimer candidate genes. Behav Genet. 2006;36(2):185–194. - PubMed
-
- de Frias CM, et al. Cholesterol and triglycerides moderate the effect of apolipoprotein E on memory functioning in older adults. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. 2007;62(2):P112–P118. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
