Bacteremia causes hippocampal apoptosis in experimental pneumococcal meningitis
- PMID: 20044936
- PMCID: PMC2824701
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-10-1
Bacteremia causes hippocampal apoptosis in experimental pneumococcal meningitis
Abstract
Background: Bacteremia and systemic complications both play important roles in brain pathophysiological alterations and the outcome of pneumococcal meningitis. Their individual contributions to the development of brain damage, however, still remain to be defined.
Methods: Using an adult rat pneumococcal meningitis model, the impact of bacteremia accompanying meningitis on the development of hippocampal injury was studied. The study comprised of the three groups: I. Meningitis (n = 11), II. meningitis with attenuated bacteremia resulting from iv injection of serotype-specific pneumococcal antibodies (n = 14), and III. uninfected controls (n = 6).
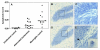
Results: Pneumococcal meningitis resulted in a significantly higher apoptosis score 0.22 (0.18-0.35) compared to uninfected controls (0.02 (0.00-0.02), Mann Whitney test, P = 0.0003). Also, meningitis with an attenuation of bacteremia by antibody treatment resulted in significantly reduced apoptosis (0.08 (0.02-0.20), P = 0.01) as compared to meningitis.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that bacteremia accompanying meningitis plays an important role in the development of hippocampal injury in pneumococcal meningitis.
Figures