(15)N Solid-state NMR spectroscopic studies on phospholamban at its phosphorylated form at ser-16 in aligned phospholipid bilayers
- PMID: 20044975
- PMCID: PMC2827642
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2009.12.020
(15)N Solid-state NMR spectroscopic studies on phospholamban at its phosphorylated form at ser-16 in aligned phospholipid bilayers
Abstract
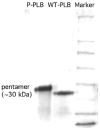
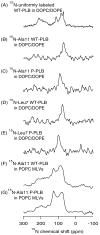
Wild-type phospholamban (WT-PLB) is a pentameric transmembrane protein that regulates the cardiac cycle (contraction and relaxation). From a physiological prospective, unphosphorylated WT-PLB inhibits sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase activity; whereas, its phosphorylated form relieves the inhibition in a mechanism that is not completely understood. In this study, site-specifically (15)N-Ala-11- and (15)N-Leu-7-labeled WT-PLB and the corresponding phosphorylated forms (P-PLB) were incorporated into 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine/2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (DOPC/DOPE) mechanically oriented lipid bilayers. The aligned (15)N-labeled Ala-11 and Leu-7 WT-PLB samples show (15)N resonance peaks at approximately 71ppm and 75ppm, respectively, while the corresponding phosphorylated forms P-PLB show (15)N peaks at 92ppm and 99ppm, respectively. These (15)N chemical shift changes upon phosphorylation are significant and in agreement with previous reports, which indicate that phosphorylation of WT-PLB at Ser-16 alters the structural properties of the cytoplasmic domain with respect to the lipid bilayers.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
References
-
- Simmerman HKB, Jones LR. Phospholamban: protein structure, mechanism of action, and role in cardiac function. Physiol Rev. 1998;78:921–947. - PubMed
-
- Ying W, Irvine SE, Beekman RA, Siminovitch DJ, Smith SO. Deuterium NMR reveals helix packing interactions in phospholamban. J Am Chem Soc. 2000;122:11125–11128.
-
- Arkin IT, Rothman M, Ludlam CFC, Aimoto S, Engelman DM, Rothschild KJ, Smith SO. Structural model of the phospholamban ion-channel complex in phospholipid-membranes. J Mol Biol. 1995;248:824–834. - PubMed
-
- Tatulian SA, Jones LR, Reddy LG, Stokes DL, Tamm LK. Secondary structure and orientation of phospholamban reconstituted in supported bilayers from polarized attenuated total-reflection FTIR spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1995;34:4448–4456. - PubMed
-
- Robia SL, Flohr NC, Thomas DD. Phospholamban pentamer quaternary conformation determined by in-gel fluorescence anisotropy. Biochemistry. 2005;44:4302–4311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

