Iontophoretic transport of charged macromolecules across human sclera
- PMID: 20045044
- PMCID: PMC2838613
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.12.046
Iontophoretic transport of charged macromolecules across human sclera
Abstract
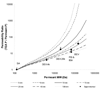
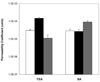
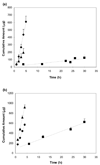
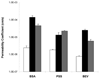
The mechanisms of transscleral iontophoresis have been investigated previously with small molecules in rabbit sclera. The objective of the present study was to examine transscleral iontophoretic transport of charged macromolecules across excised human sclera. Passive and 2mA iontophoretic transport experiments were conducted in side-by-side diffusion cells with human sclera. The effects of iontophoresis upon transscleral transport of model permeants bovine serum albumin (BSA) and polystyrene sulfonic acid (PSS) as well as a model drug bevacizumab (BEV) were determined. Passive and iontophoretic transport experiments of tetraethylammonium (TEA) and salicylic acid (SA) and passive transport experiments of the macromolecules served as the controls. The results of iontophoresis enhanced transport of TEA and SA across human sclera were consistent with those in a previous rabbit sclera study. For the iontophoretic transport of macromolecules BSA and BEV, higher iontophoretic fluxes were observed in anodal iontophoresis as compared to passive and cathodal iontophoresis. This suggests the importance of electroosmosis. For the polyelectrolyte PSS, higher iontophoretic flux was observed in cathodal iontophoresis compared to anodal iontophoresis. Both electroosmosis and electrophoresis affected iontophoretic fluxes of the macromolecules; the relative contributions of electroosmosis and electrophoresis were a function of molecular size and charge of the macromolecules.
Copyright (c) 2009 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Ambati J, Canakis CS, Miller JW, Gragoudas ES, Edwards A, Weissgold DJ, Kim I, Delori FC, Adamis AP. Diffusion of high molecular weight compounds through sclera. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000;41:1181–1185. - PubMed
-
- Behar-Cohen F, El Aouni A, Gautier S, David G, Davis J, Chapon P, Parel JM. Transscleral coulomb-controlled iontophoresis of methylprednisolone into the rabbit eye: Influence of duration of treatment, current intensity and drug concentration on ocular tissue and fluid levels. Exp. Eye Res. 2002;74:51–59. - PubMed
-
- Behar-Cohen FF, Parel JM, Pouliquen Y, Thillaye-Goldenberg B, Goureau O, Heydolph S, Courtois Y, De Kozak Y. Iontophoresis of dexamethasone in the treatment of endotoxin-induced-uveitis in rats. Exp Eye Res. 1997;65:533–545. - PubMed
-
- Bockris JOM, Reddy AKN. Modern Electrochemistry. 2nd. New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers; 1998.
-
- Cruysberg LPJ, Nuijts RMMA, Geroski DH, Koole LH, Hendrikse F, Edelhauser HF. In vitro human scleral permeability of fluorescein, dexamethasonefluorescein, methotrexate-fluorescein and rhodamine 6G and the use of a coated coil as a new drug delivery system. J. Ocul. Pharmaco. Ther. 2002;18:559–569. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

