Intermediate filaments take the heat as stress proteins
- PMID: 20045331
- PMCID: PMC2843093
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2009.11.004
Intermediate filaments take the heat as stress proteins
Abstract
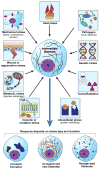
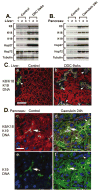
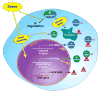
Intermediate filament (IF) proteins and heat shock proteins (HSPs) are large multimember families that share several features, including protein abundance, significant upregulation in response to a variety of stresses, cytoprotective functions, and the phenocopying of several human diseases after IF protein or HSP mutation. We are now coming to understand that these common elements point to IFs as important cellular stress proteins with some roles akin to those already well-characterized for HSPs. Unique functional roles for IFs include protection from mechanical stress, whereas HSPs are characteristically involved in protein folding and as chaperones. Shared IF and HSP cytoprotective roles include inhibition of apoptosis, organelle homeostasis, and scaffolding. In this report, we review data that corroborate the view that IFs function as highly specialized cytoskeletal stress proteins that promote cellular organization and homeostasis.
Figures
References
-
- Morimoto RI, Santoro MG. Stress-inducible responses and heat shock proteins: new pharmacologic targets for cytoprotection. Nat Biotechnol. 1998;16(9):833–8. - PubMed
-
- Akerfelt M, et al. Heat shock factors at a crossroad between stress and development. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1113:15–27. - PubMed
-
- van Noort JM. Stress proteins in CNS inflammation. J Pathol. 2008;214(2):267–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

