Differential regulation of inducible and endothelial nitric oxide synthase by kinin B1 and B2 receptors
- PMID: 20045558
- PMCID: PMC2830320
- DOI: 10.1016/j.npep.2009.12.004
Differential regulation of inducible and endothelial nitric oxide synthase by kinin B1 and B2 receptors
Abstract
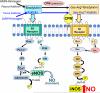
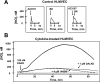
Kinins are vasoactive peptides that play important roles in cardiovascular homeostasis, pain and inflammation. After release from their precursor kininogens, kinins or their C-terminal des-Arg metabolites activate two distinct G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR), called B2 (B2R) or B1 (B1R). The B2R is expressed constitutively with a wide tissue distribution. In contrast, the B1R is not expressed under normal conditions but is upregulated by tissue insult or inflammatory mediators. The B2R is considered to mediate many of the acute effects of kinins while the B1R is more responsible for chronic responses in inflammation. Both receptors can couple to Galphai and Galphaq families of G proteins to release mediators such as nitric oxide (NO), arachidonic acid, prostaglandins, leukotrienes and endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor and can induce the release of other inflammatory agents. The focus of this review is on the different transduction events that take place upon B2R and B1R activation in human endothelial cells that leads to generation of NO via activation of different NOS isoforms. Importantly, B2R-mediated eNOS activation leads to a transient ( approximately 5min) output of NO in control endothelial cells whereas in cytokine-treated endothelial cells, B1R activation leads to very high and prolonged ( approximately 90min) NO production that is mediated by a novel signal transduction pathway leading to post-translational activation of iNOS.
Keywords: bradykinin; eNOS; endothelial cells; iNOS; kinin B1 receptor; kinin B2 receptor; nitric oxide; nitric oxide synthase.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- AbdAlla S, Jarnagin K, Muller-Esterl W, Quitterer U. The N-terminal amino group of [Tyr8]bradykinin is bound adjacent to analogous amino acids of the human and rat B2 receptor. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:27382–27387. - PubMed
-
- Abraham WM, Scuri M, Farmer SG. Peptide and non-peptide bradykinin receptor antagonists: role in allergic airway disease. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006;533:215–221. - PubMed
-
- Adomeit A, Graness A, Gross S, Seedorf K, Wetzker R, Liebmann C. Bradykinin B(2) receptor-mediated mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in COS-7 cells requires dual signaling via both protein kinase C pathway and epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:5289–5297. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aktan F. iNOS-mediated nitric oxide production and its regulation. Life Sci. 2004;75:639–653. - PubMed
-
- Alfie ME, Sigmon DH, Pomposiello SI, Carretero OA. Effect of high salt intake in mutant mice lacking bradykinin-B2 receptors. Hypertension. 1997;29:483–487. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

